You are here: Urology Textbook > Kidneys > Calyceal diverticulum
Calyceal Diverticulum
Definition
A calyceal diverticulum is a renal cystic cavity. It is lined with urothelium and has (or had) a connection to a pyelocalyceal system. Synonym: pyelogenic cyst.
Epidemiology of calyceal diverticula:
4,5:1000 (from studies with intravenous urography)
Etiology of Calyceal Diverticula
Congenital:
Result of failed degeneration of ureteric bud branches.
Acquired:
Calyceal diverticula may develop from a cortical kidney abscess, a cortical cyst, or from calyceal obstruction. Complications of urinary stasis are recurrent urinary tract infections, milk of calcium, or nephrolithiasis.
Signs and Symptoms of Calyceal Diverticula
- Pain, hematuria, or recurrent infections
- Nephrolithiasis
- Cystic mass in imaging
Diagnostic Workup
Renal sonography:
Renal ultrasound reveals a cystic structure near a calyx, often filled with echogenic content (milk of calcium, changing with the position of the examination).
CT:
Best imaging procedure for the diagnosis of unclear renal cysts [fig. Calyceal diverticulum in CT].
Intravenous Urography:
Caliceal diverticula are often visible on the plain KUB abdominal X-ray (milk of calcium). Otherwise, the calyceal diverticulum presents as a mass, pooling of contrast medium is only sometimes visible within a few minutes. Late films after 1–3 hours are helpful.
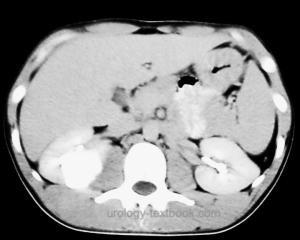 |
Retrograde pyelography:
Perform retrograde pyelography before treatment of nephrolithiasis or during invasive diagnostic workup of hematuria [fig. Calyceal diverticulum in retrograde pyelography].
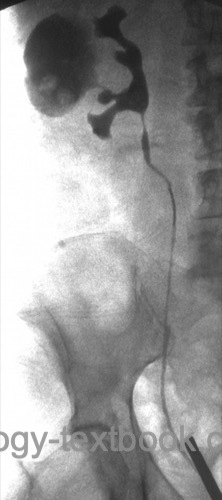 |
Diagnostic Puncture:
The creatinine concentration of the aspirated fluid is significantly higher than the serum creatinine concentration. A cytological examination is an option to exclude a malignant cyst.
Differential Diagnosis:
Simple renal cyst.Treatment of Calyceal Diverticula
Endoscopic Therapy:
First, obtain percutaneous access into the calyceal diverticulum and remove calyceal stones, if present. Consider fulguration of the diverticular mucosa to induce shrinkage. Dilate the connection between the diverticulum and calyx to secure urine drainage. Place a thick nephrostomy into the renal pelvis.
Open or Laparoscopic Surgery:
Partial nephrectomy: removal of the diverticulum with corresponding renal parenchyma.
| Renal malrotation | Index | Megacalycosis |
Index: 1–9 A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z
References
Waingankar, N., Hayek, S., Smith, A. D., and Okeke, Z. (2014). Calyceal Diverticula: A Comprehensive Review. Reviews in Urology, 16(1), 29-43. https://doi.org/https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4004282/
 Deutsche Version: Kelchdivertikel
Deutsche Version: Kelchdivertikel
Urology-Textbook.com – Choose the Ad-Free, Professional Resource
This website is designed for physicians and medical professionals. It presents diseases of the genital organs through detailed text and images. Some content may not be suitable for children or sensitive readers. Many illustrations are available exclusively to Steady members. Are you a physician and interested in supporting this project? Join Steady to unlock full access to all images and enjoy an ad-free experience. Try it free for 7 days—no obligation.
New release: The first edition of the Urology Textbook as an e-book—ideal for offline reading and quick reference. With over 1300 pages and hundreds of illustrations, it’s the perfect companion for residents and medical students. After your 7-day trial has ended, you will receive a download link for your exclusive e-book.