You are here: Urology Textbook > Kidneys > Renal cell carcinoma
Renal Cell Carcinoma: Definition, Epidemiology, and Etiology
- Renal cell carcinoma: Definition, Epidemiology and Etiology
- Renal cell carcinoma: Pathology
- Renal cell carcinoma: Diagnostic workup
- Renal cell carcinoma: Surgical Treatment
- Renal cell carcinoma: Targeted therapy of advanced disease
Definition of Renal Cell Carcinoma
Renal cell carcinoma is the most common malignant tumor of the kidney arising from different epithelial parts from the nephron. Review literature: EAU Guidelines, German S3 Guidelines..
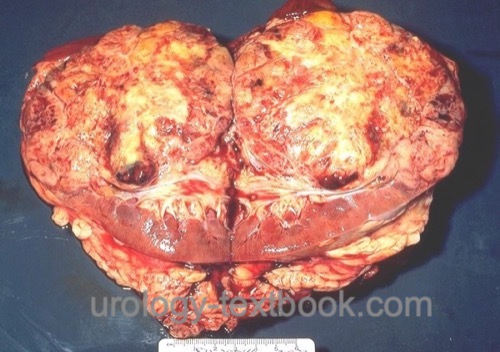 |
Epidemiology of Renal Cell Carcinoma
Cancer statistics:
- 3% of all tumors
- Third most common malignant urological malignancy, position 10 in the cancer statistics of the EU 2008.
- The incidence of renal cell carcinoma increased in the last decades but has stabilized recently.
Mortality of renal cell carcinoma:
Mortality is declining; 2018 figures of the standardized mortality rate for Germany are 5/100.000 for men and 2/100.000 for women.
Incidence of renal cell carcinoma:
Incidence of RCC in Germany (2018): 15/100.000 for men and 8/100.000 for women. Rising incidence with age, with peak incidence at 70–75 years, but RCC can also occur in children.
Tumor stage:
Most kidney tumors are diagnosed in stages T1 and T2. Advanced T4 tumors are rare at first presentation (2%).
Pathogenesis of Renal Cell Carcinoma
Origin:
Clear cell renal cell carcinoma originates from cells of the proximal tubule. Other histological types arise from more distal parts of the nephron.
Carcinogenic substances.
Risk factors for RCC are smoking (RR 1.4–2.3 dose-dependent), chewing tobacco, cadmium, lead, petrochemical substances, solvents (trichloroethylene), Thorotrast, tar, and wood preservatives.
Epidemiological risk factors for renal cell carcinoma:
Terminal renal insufficiency (RR 3–6), obesity (RR 2.7), arterial hypertension, low social status, urban origin, smoking (RR 1.4–2.3), increased consumption of fats and proteins in the diet. Protective factors are moderate alcohol consumption and sportive activity.
Molecular biology:
Mutations of the VHL gene are detectable in most sporadic renal cell carcinomas (see below).
Familial renal cell carcinoma
The risk of renal cell cancer for first-degree relatives of affected patients is approximately doubled, this suggests hereditary causes. Several genetic variations for an increased risk with low penetrance are known, e.g., variations of HIF 2 alpha (hypoxia-inducible factor). About 5–8% of all renal cell carcinomas are inherited. Below mentioned rare genetic syndromes usually follow an autosomal dominant inheritance (Verine et al., 2010).
Hippel-Lindau disease and renal cell carcinoma:
Hippel-Lindau disease shows an autosomal dominant inheritance with a high risk for clear cell renal cell carcinoma, please see section "von Hippel-Lindau syndrome" for details. The responsible VHL gene mutation is located on chromosome 3. The VHL protein is a tumor suppressor protein. The tumors develop according to the Knudson theory of two hits: one diseased gene is inherited on one chromosome, and a spontaneous mutation on the second chromosome causes the second hit (change of DNA). Tumors arise only when both VHL genes on both chromosomes are mutated. The probability of renal cell carcinoma occurrence (penetrance) in Hippel-Lindau disease is 25–70%. In comparison to sporadic renal cell cancer, RCC in von Hippel-Lindau patients occurs earlier, often with multifocal lesions, and presents with changes in other organs (CNS, retina, adrenal glands, cystic changes in the parenchymatous organs).
Hereditary papillary renal cell carcinoma (HPRCC):
Hereditary papillary renal cell carcinoma (HPRCC) is an autosomal dominant disease that leads to papillary renal cell carcinoma with basophilic papillary histology (type 1). Mutations in the MET protooncogene have been described on chromosome 7; MET encodes the hepatocyte growth factor receptor (HGFR). Patients with HPRCC do not have an increased risk for other tumor entities. Genetic diagnosis is possible.
Tuberous sclerosis:
Patients with tuberous sclerosis harbor an increased risk for renal cell carcinoma [see section "Tuberous sclerosis"].
Birt-Hogg-Dubé Syndrome:
Birt-Hogg-Dubé Syndrome is a genetic disorder causing benign skin tumors (fibrofolliculomas), renal tumors (chromophobe renal cell carcinoma, oncocytoma, or seldom clear cell renal cell carcinoma), and pulmonary cysts with the risk of spontaneous pneumothorax. About 25% of the patients develop kidney tumors. The responsible gene (FLCN) encodes a protein (Folliculin) with tumor suppressor function. The genetic defect is inherited autosomal dominant, and genetic diagnosis is possible (Menko et al., 2009).
Hereditary leiomyomatosis and renal cell carcinoma syndrome:
First publication of the syndrome in 2001 with cutaneous and uterine leiomyomas, and particularly aggressive renal cell carcinomas. The histologic subtype is either type 2 papillary carcinoma or collecting duct carcinoma. The HLRCC syndrome is caused by mutations in the fumarate hydratase gene (FH) and is inherited autosomal dominant (Badeloe et al., 2009). A genetic diagnosis is possible. The exact connection between the enzyme of the citric acid cycle and renal cell carcinoma is still unclear. Unlike in other familial syndromes, renal tumors in HLRCC syndrome should be treated immediately since they metastasize early.
Tumor Biology of Renal Cell Carcinoma
Immunobiology:
Renal cell carcinoma induces an obvious immunological reaction, several immunological mechanisms have been successfully used in therapy:
- Spontaneous regression of metastases of RCC after cytoreductive tumor nephrectomy (in 1–7%) is explained by immunological factors. The remission can be stable over a long period of time.
- Interferon and interleukin: immunotherapy with INF and IL leads to a response rate of 10–20%.
- Immune checkpoints: the activation of immune checkpoint receptors lead to the inhibition and weakening of the cellular immune response. This is a physiological function to prevent autoimmune diseases. Various receptors were identified: PD-1 receptor (PD for programmed cell death) or CTLA-4 (CTLA for cytotoxic T lymphocyte antigen) on T lymphocytes with corresponding ligands such as PD-L1. Several tumors including RCC uses immune checkpoints to induce immune tolerance. The inhibition of the immune checkpoints with specific antibodies leads to a clear response and improvement of survival in advanced renal cell carcinoma.
Regulation of proliferation and tumor vascularization:
The rich neovascularization is triggered by the overexpression of VEGF. Proliferation is regulated through increased expression of TGF-$\alpha $, EGF receptors, up-regulation of Ras-Raf-MAPK signal transduction, increased expression of MET protooncogene (receptor tyrosine kinase for the hepatocyte growth factor), activation of mTOR (mammalian target of Rapamycin), an important signal transduction pathway of cell growth, angiogenesis, energy balance and apoptosis. The regulation of proliferation and vascularization can be influenced with inhibitors of signal transduction to improve the prognosis of patients with metastasis.
Regulation of cell adhesion:
Changed intracellular processing of fibronectin, increased expression of proteases such as plasmin and the matrix metalloproteinases, reduced expression of E-cadherin and cadherin-6.
Resistance to chemotherapy:
The expression of multi-drug resistance protein-1 (MDR-1) has been made responsible for the lack of sensitivity to chemotherapy. MDR-1 (P-glycoprotein) is a transmembrane protein that pumps many foreign substances out of the cell.
| Angiomyolipoma | Index | Pathology of Kidney Cancer |
Index: 1–9 A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z
References
Algaba, F.; Akaza, H.; López-Beltrán, A.; Martignoni,
G.; Moch, H.; Montironi, R. & Reuter, V.
Current pathology keys of
renal cell carcinoma.
Eur Urol, 2011, 60, 634-643.
Badeloe, S. & Frank, J.
Clinical and molecular
genetic aspects of hereditary multiple cutaneous leiomyomatosis.
Eur
J Dermatol, 2009, 19, 545-551
DGU; DKG; DKG & Leitlinienprogramm Onkologie Diagnostik, Therapie und Nachsorge des Nierenzellkarzinoms, Langversion 4.02023 https://www.leitlinienprogramm-onkologie.de/leitlinien/nierenzellkarzinom/.
Eble, J. N.; Sauter, G.; Epstein, J. I. & Sesterhenn,
I. A. (ed.)
World Health Organization classification of tumours.
Pathology and genetics of tumours of the urinary system and male genital
organs
IARC Press, 2004.
Hock u.a. 2002 HOCK, L. M. ; LYNCH, J. ;
BALAJI, K. C.:
Increasing incidence of all stages of kidney cancer in the last 2
decades in the United States: an analysis of surveillance, epidemiology and
end results program data.
In: J Urol
167 (2002), Nr. 1, S. 57–60
Ljungberg, B.; Albiges, L.; Bensalah, K.; Bex, A.;
Giles, R.; Hora, M.; Kuczyk, M.; Lam, T.; L.Marconi; Merseburger, A.;
Powles, T.; Staehler, M. & Volpe, A.
EAU Guidelines on Renal Cell Carcinoma
2018. https://uroweb.org/guidelines/renal-cell-carcinoma/
Ljungberg, B.; Campbell, S. C.; Cho, H. Y.; Jacqmin,
D.; Lee, J. E.; Weikert, S. & Kiemeney, L. A.
The epidemiology of
renal cell carcinoma.
Eur Urol, 2011, 60, 615-621.
Menko, F. H.; van Steensel, M. A. M.; Giraud, S.;
Friis-Hansen, L.; Richard, S.; Ungari, S.; Nordenskjöld, M.; Hansen, T.
V.; Solly, J.; Maher, E. R. & Consortium, E. B.
Birt-Hogg-Dubé
syndrome: diagnosis and management.
Lancet Oncol, 2009,
10, 1199-1206.
Steffens, S.; Janssen, M.; Roos, F. C.; Becker, F.;
Schumacher, S.; Seidel, C.; Wegener, G.; Thüroff, J. W.; Hofmann, R.;
Stöckle, M.; Siemer, S.; Schrader, M.; Hartmann, A.; Kuczyk, M. A.;
Junker, K. & Schrader, A. J.
Incidence and long-term prognosis of
papillary compared to clear cell renal cell carcinoma - a multicentre study.
Eur
J Cancer, 2012, 48, 2347-2352.
Storkel u.a. 1997 STORKEL, S. ; EBLE, J. N. ;
ADLAKHA, K. ; AMIN, M. ; BLUTE, M. L. ;
BOSTWICK, D. G. ; DARSON, M. ; DELAHUNT, B. ;
ICZKOWSKI, K.:
Classification of renal cell carcinoma: Workgroup No. 1. Union
Internationale Contre le Cancer (UICC) and the American Joint Committee on
Cancer (AJCC).
In: Cancer
80 (1997), Nr. 5, S. 987–9
Verine, J.; Pluvinage, A.; Bousquet, G.; Lehmann-Che,
J.; de Bazelaire, C.; Soufir, N. & Mongiat-Artus, P.
Hereditary
renal cancer syndromes: an update of a systematic review.
Eur Urol, 2010,
58, 701-710.
 Deutsche Version: Nierenzellkarzinom
Deutsche Version: Nierenzellkarzinom
Urology-Textbook.com – Choose the Ad-Free, Professional Resource
This website is designed for physicians and medical professionals. It presents diseases of the genital organs through detailed text and images. Some content may not be suitable for children or sensitive readers. Many illustrations are available exclusively to Steady members. Are you a physician and interested in supporting this project? Join Steady to unlock full access to all images and enjoy an ad-free experience. Try it free for 7 days—no obligation.
New release: The first edition of the Urology Textbook as an e-book—ideal for offline reading and quick reference. With over 1300 pages and hundreds of illustrations, it’s the perfect companion for residents and medical students. After your 7-day trial has ended, you will receive a download link for your exclusive e-book.