You are here: Urology Textbook > Surgery (procedures) > ESWL
ESWL: Technique and Complications of Extracorporeal Shock Wave Lithotripsy
Extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy (ESWL) is a noninvasive technical procedure in urology that enables the disintegration of urinary stones by shock waves without anesthesia. ESWL was developed in Munich (Chaussy et al., 2002 (Reprint from 1982)).
Indications for ESWL
Kidney stones less than 2 cm in diameter may be treated with ESWL. Ureteral stones in the proximal ureter are still also treatable. Locating and positioning the shock source for distal ureteral stones is more complex but possible (Bach u.a., 2011).
Contraindications to ESWL
Absolute contraindications to ESWL:
- Coagulation disorders
- Platelet aggregation inhibitors (e.g., ASS)
- Pregnancy
- Aortic aneurysm
- Untreated urinary tract infection
- Stone localization with imaging during ESWL is not possible.
Relative contraindications to ESWL:
- Urinary tract obstruction. ESWL on small ureteral stones may be done even with urinary tract obstruction
Physical Principles of Extracorporeal Shock Wave Lithotripsy (ESWL)
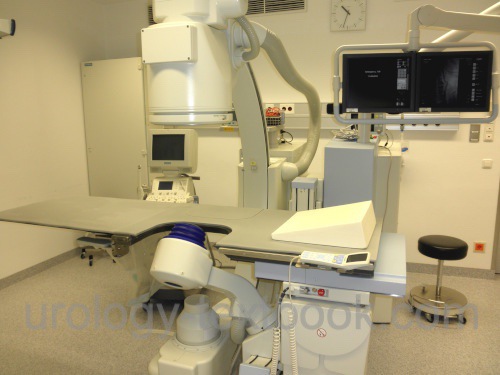 |
The principle of ESWL is externally generated shock waves, which are directed into the patient's body and focused on the target (kidney or ureter stone). Three different generator types for shock wave lithotripsy exist:
Electromagnetic ESWL:
The shock wave is generated by an electromagnetic coil, which moves a membrane (like a loudspeaker). An acoustic lens system reflects and focuses the shock wave. Examples: Dornier Doli, Lithostar Siemens.
Electrohydraulic ESWL:
The shock wave is generated by an underwater spark discharge, which is reflected by an ellipsoid. Example: Dornier HM3.
Piezoelectric ESWL:
A piezoelectric crystal is mechanically deformed if electricity is applied. The crystals are aligned along a spherical dish, allowing the shock waves to focus. Example: PiezoLith of Wolff.
Technique of Extracorporeal Shock Wave Lithotripsy
Prerequisites for ESWL:
- Treat significant upper urinary tract obstruction with a ureteral stent (DJ) before ESWL. Consider the insertion of a DJ also before treating large kidney stones since the fragments may obstruct the ureter ("Steinstraße"). Small ureteral stones with moderate hydronephrosis may be treated without DJ since fragmentation may resolve the hydronephrosis.
- Coagulation and platelet function should be normal: PTT, PT, and blood count.
- Normal blood pressure
- Sterile urine; perioperative antibiotic prophylaxis is unnecessary.
- The imaging system can locate the stone
- Bubble-free coupling of the shock source to the patient with ample gel.
Analgesia:
The better the analgesia, the higher the stone-free results after ESWL due to minimizing patient movements (pain, respiration). The minimum is a conscious sedation with, e.g., midazolam and piritramide.
Monitoring of the patient:
Monitor the oxygen saturation, ECG, and blood pressure during extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy.
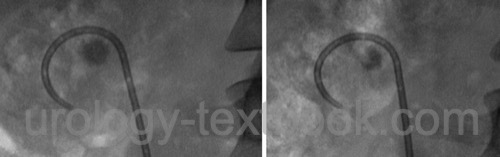
Imaging for Stone Localization:
Imaging for stone localization can be done with ultrasound, fluoroscopy, or a combination of both. The localization must be checked regularly during treatment, as patients often move due to pain.
Dosage of Shock Waves:
2000–4000 shock waves are used with a 60–120/min frequency. Comparative studies found a higher efficacy of ESWL with a lower frequency of shock waves (60 vs. 120/min). Shock waves generate microscopic cavitation bubbles in the focus, which rapidly disintegrate spontaneously. With a high frequency of shock waves, the energy of the next shock wave is lost due to the cavitation bubbles of the former shock wave, leaving the kidney stone intact.
The power of the shock wave depends on the patient's pain threshold or is set according to the recommended maximum value by the manufacturer of the ESWL machine. A pause of several days should be in between treatment sessions.
Follow-up after ESWL
Imaging (ultrasound, KUB X-ray) is necessary to evaluate stone clearance, upper urinary tract obstruction or to detect renal hematoma. Upper urinary tract obstruction symptoms are treated with NSAID (e.g., Diclofenac 75 mg 1-0-1) and alpha blockers (e.g., tamsulosin 0,4 mg 1-0-0, off-label).
 |
Complications after ESWL
Blood pressure:
Low blood pressure with nausea and vomiting is possible.
Bleeding:
Bleeding leads to hematuria (often), retroperitoneal hematoma, or pseudoaneurysm of the renal arteries (rare). The extent of renal injury depends on the number of shock waves, shock wave energy, size, and location of the stone. Risk factors of the patient for retroperitoneal hematoma are coagulation disorders, platelet dysfunction, use of antiplatelet agents, or arterial hypertension.
Urinary tract obstruction:
Fragments of disintegrated stones may obstruct the ureter ("Steinstraße") and cause urinary colic.
Infections:
Urinary tract infection with fever. Urosepsis is possible, especially when it comes to upper urinary tract obstruction.
Renal Failure:
Renal failure is a rare complication after ESWL, caused by the combination of the abovementioned complications. Singularly, a nephrectomy is necessary due to complications (loss of kidney function, renal abscess, or massive hemorrhage).
| Urologic Surgery | Index | Open Nephroureterectomy |
Index: 1–9 A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z
References
Bach, C. & Buchholz, N.
Shock wave lithotripsy
for renal and ureteric stones
Eur Urol Suppl, 2011,
10, 423-432.
Chaussy u.a. 2002 CHAUSSY, C. ; SCHMIEDT, E. ;
JOCHAM, D. ; BRENDEL, W. ; FORSSMANN, B. ;
WALTHER, V.:
First clinical experience with extracorporeally induced destruction
of kidney stones by shock waves. 1982.
In: J Urol
167 (2002), Nr. 5, S. 1957–60
Lawler AC, Ghiraldi EM, Tong C, Friedlander JI. Extracorporeal Shock Wave Therapy: Current Perspectives and Future Directions. Curr Urol Rep. 2017 Apr;18(4):25. doi: 10.1007/s11934-017-0672-0.
Setthawong V, Srisubat A, Potisat S, Lojanapiwat B, Pattanittum P. Extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy (ESWL) versus percutaneous nephrolithotomy (PCNL) or retrograde intrarenal surgery (RIRS) for kidney stones. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2023 Aug 1;8(8):CD007044. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD007044.pub4.
 Deutsche Version: ESWL
Deutsche Version: ESWL
Urology-Textbook.com – Choose the Ad-Free, Professional Resource
This website is designed for physicians and medical professionals. It presents diseases of the genital organs through detailed text and images. Some content may not be suitable for children or sensitive readers. Many illustrations are available exclusively to Steady members. Are you a physician and interested in supporting this project? Join Steady to unlock full access to all images and enjoy an ad-free experience. Try it free for 7 days—no obligation.
New release: The first edition of the Urology Textbook as an e-book—ideal for offline reading and quick reference. With over 1300 pages and hundreds of illustrations, it’s the perfect companion for residents and medical students. After your 7-day trial has ended, you will receive a download link for your exclusive e-book.