You are here: Urology Textbook > Kidneys > Perinephric abscess
Symptoms, Diagnosis and Treatment of Perinephric Abscess
Definition
A perinephric abscess is a collection of pus within the renal fascia. Review literature: (Angel et al., 2003) (Shu et al., 2004)
Etiology
Gram-negative Bacteria:
Perinephric abscesses are most commonly caused by gram-negative bacteria such as E. coli and Proteus. Perinephric abscesses with gram-negative bacteria usually result from the rupture of a renal abscess with a cortical location. Nephrolithiasis is a risk factor.
Staphylococci:
Before the antibiotic era, perinephric abscesses were often caused by the hematogenous spread of staphylococci. Today's risk groups for the hematogenous spread of staphylococci are intravenous drug abuse, intensive care, dialysis patients, valvular heart disease, and endocarditis.
.Signs and Symptoms of a Perinephric Abscess
In contrast to a renal abscess, signs and symptoms of a perinephric abscess have a slow onset and are unspecific. Patients usually present with symptoms of more than one week, complaining about fever, flank pain or abdominal pain, night sweat and chills. More than 30% are afebrile.
Perinephric Abscess: Diagnostic Workup
Urine culture:
Urine culture can only identify the responsible bacteria in 30%.
Laboratory tests:
Blood culture (positive in 50%). Blood count, coagulation tests (PTT, PT), CRP, liver enzymes, creatinine. In suspected urosepsis, determine sepsis parameters such as blood gas testing, procalcitonin, AT III, and fibrinogen.
Ultrasonography:
Sonographic signs for a perinephric abscess in renal ultrasound are a perirenal hypoechoic area, which may have inclusions of air (echogenic reflex with dorsal shadowing).
Computed tomography:
CT is the diagnostic test of choice [fig. perinephric abscess]. The perinephric abscess appears as a hypodense area. After administration of contrast medium, the abscess capsule has a ring-like enhancement. Air inclusion is possible.
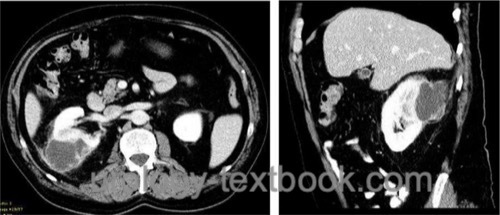 |
Intravenous urography:
Intravenous urography is not very helpful in suspected perinephric abscess. If done, abdominal X-ray may show an absent psoas shadow, a perinephric mass, retroperitoneal air surrounding the kidney, and nephrolithiasis. The excretion of contrast medium is often without pathological findings.
Treatment of a Perinephric Abscess
Treatment of a perinephric abscess consists of parenteral antibiotics and abscess drainage:
- Parenteral antibiotics: e.g., amoxicillin and clavulanic acid 2,2 g 1–1–1 IV in combination with gentamicin 3 mg/kg 1–0–0 IV Alternatives are third-generation cephalosporins.
- Abscess drainage: renal abscess larger than 3 cm diameter should be drained. Pus is sent for identification of bacteria and antibiotic resistance testing. Renal abscess larger than 5 cm diameter may need repeated or several parallel pigtail drains.
- In advanced disease, surgical drainage or nephrectomy is rarely necessary, depending on renal function.
| Renal abscess | Index | Kidneys |
Index: 1–9 A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z
References
Angel u.a. 2003 ANGEL, C. ; SHU, T. ;
GREEN, J. ; ORIHUELA, E. ; RODRIQUEZ, G. ;
HENDRICK, E.:
Renal and peri-renal abscesses in children: proposed
physio-pathologic mechanisms and treatment algorithm.
In: Pediatr Surg Int
19 (2003), Nr. 1–2, S. 35–9
Shu u.a. 2004 SHU, T. ; GREEN, J. M. ;
ORIHUELA, E.:
Renal and perirenal abscesses in patients with otherwise anatomically
normal urinary tracts.
In: J Urol
172 (2004), Nr. 1, S. 148–50
 Deutsche Version: Perinephritischer Abszess
Deutsche Version: Perinephritischer Abszess
Urology-Textbook.com – Choose the Ad-Free, Professional Resource
This website is designed for physicians and medical professionals. It presents diseases of the genital organs through detailed text and images. Some content may not be suitable for children or sensitive readers. Many illustrations are available exclusively to Steady members. Are you a physician and interested in supporting this project? Join Steady to unlock full access to all images and enjoy an ad-free experience. Try it free for 7 days—no obligation.
New release: The first edition of the Urology Textbook as an e-book—ideal for offline reading and quick reference. With over 1300 pages and hundreds of illustrations, it’s the perfect companion for residents and medical students. After your 7-day trial has ended, you will receive a download link for your exclusive e-book.