You are here: Urology Textbook > Urologic surgery > Flank incision
Flank Incision: Indications, Anatomy and Surgical Technique
 |
Urologic Indications for a Flank Incision
Kidney Surgery
- Simple nephrectomy or radical nephrectomy
- Partial nephrectomy
- Open nephrolithotomy
Surgery of the Ureter
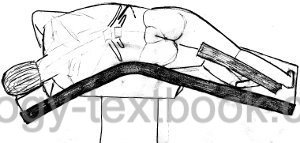
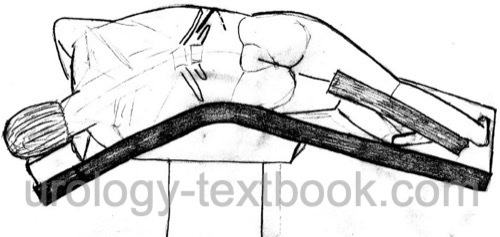
Patient positioning:
The patient is placed in a lateral position on a flexed operation table, see fig. flank incision.
 |
Flank Incision: Surgical Technique
- The skin incision follows the 11th intercostal space (between 11th and 12th rib).
- Split the external oblique abdominal muscle in the direction along the muscle fibers just above the 12th rib. Portions of the serratus anterior muscle and latissimus dorsi muscle are transected as necessary to expose the ribs.
- Transect the internal oblique abdominal muscle perpendicular to the muscle fibers with electrosurgical cautery. The transverse abdominal muscle is split between the muscle fibers.
- Avoid injury to the subcostal nerve; a flank incision below the 12th rib is not advisable.
- The transection of the intercostal muscles is done with care not to injure the pleura. Insert a retractor between the ribs (without breaking them).
- Open the renal fascia and bluntly dissect the layer between the perirenal fat and the psoas muscle. Dissect the peritoneum of the perirenal fat to expose the kidney from all sides.
Wound closure:
The muscles are closed in two layers, either with a continuous running suture (monofilament, elastic, slowly absorbable, suture size USP 0 or 1) or an interrupted suture. The first layer includes the transverse abdominal muscle and the internal oblique abdominal muscle. The second layer closes the external oblique, serratus anterior, and latissimus dorsi muscle.
| Subcostal incision | Index | Thoracoabdominal incision |
Index: 1–9 A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z
References
J. L. Duque, K. R. Loughlin, and S. Kumar, “Morbidity of flank incision for renal donors.,” Urology, vol. 54, no. 5, pp. 796–801, 1999.
J. A. Smith, S. S. Howards, G. M. Preminger, and R. R. Dmochowski, Hinman’s Atlas of Urologic Surgery Revised Reprint. Elsevier, 2019.
M. C. Kriegmair et al., “Single- vs multiple-layer wound closure for flank incisions: results of a prospective, randomised, double-blinded multicentre study.,” BJU international, vol. 127, no. 1, pp. 64–70, 2021.
 Deutsche Version: Flankenschnitt
Deutsche Version: Flankenschnitt
Urology-Textbook.com – Choose the Ad-Free, Professional Resource
This website is designed for physicians and medical professionals. It presents diseases of the genital organs through detailed text and images. Some content may not be suitable for children or sensitive readers. Many illustrations are available exclusively to Steady members. Are you a physician and interested in supporting this project? Join Steady to unlock full access to all images and enjoy an ad-free experience. Try it free for 7 days—no obligation.
New release: The first edition of the Urology Textbook as an e-book—ideal for offline reading and quick reference. With over 1300 pages and hundreds of illustrations, it’s the perfect companion for residents and medical students. After your 7-day trial has ended, you will receive a download link for your exclusive e-book.