You are here: Urology Textbook > Surgery (procedures) > Simple retropubic prostatectomy
Retropubic Simple Prostatectomy: Steps of the Millin Technique
Indications for Millin's Simple Prostatectomy
Surgical treatment of benign prostatic hyperplasia is necessary in cases of recurrent urinary retention, recurrent urinary tract infections, recurrent hematuria, bladder stones, postrenal kidney failure, and large bladder diverticula. The most common indication for surgical therapy is moderate to severe symptoms of BPH, which are inadequately relieved with medication and limit the patient's quality of life.
The surgical technique of transvesical simple prostatectomy [fig. principle of suprapubic prostatectomy] is indicated for very large adenoma (>75 ml) or contraindications for lithotomy position. The retropubic approach offers the advantage of better hemostasis and improved vision for the apical adenomectomy. Inguinal hernia may be treated simultaneously with a simple prostatectomy. The retropubic approach is not ideal for large middle lobes and significant obesity. Consider transvesical simple prostatectomy for large bladder stones or bladder diverticula.
Contraindications to Retropubic Prostatectomy
Prostate cancer, low life expectancy, coagulation disorders, and untreated urinary tract infection.
Surgical Technique of Millin's Simple Prostatectomy
Preoperative Patient Preparation
- Exclude or treat urinary tract infections
- Perioperative antibiotic prophylaxis
- General anesthesia or spinal anesthesia
- Supine position with slight hyperextension of the lumbar spine
- Disinfection and draping
- Insert a 22 CH irrigation catheter.
Surgical Approach:
- Lower midline incision or Pfannenstiel incision
- Cut the linea alba
- After blunt dissection of the retropubic space, insert a wound retractor and a malleable blade to displace the bladder superiorly.
- Surgical exposure of the prostate is comparable to radical prostatectomy: incision of the endopelvic fascia, dissection of lateral aspects of the puboprostatic ligament, ligature of the dorsal venous plexus at the apex and near the bladder neck. In addition, the lateral prostate pedicles with significant arterial supply to the prostate are controlled with figure of eight sutures (do not incorporate the ureters).
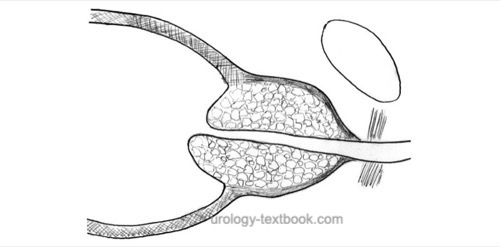
Dissection of the Prostatic Adenoma:
- Transverse capsulotomy.
- Blunt dissection of the ventral aspect of the adenoma.
- Divide the anterior commissure from the bladder neck to the apex; this separates the lateral lobes of the prostate anteriorly, and the prostatic urethra becomes visible. Retract the catheter.
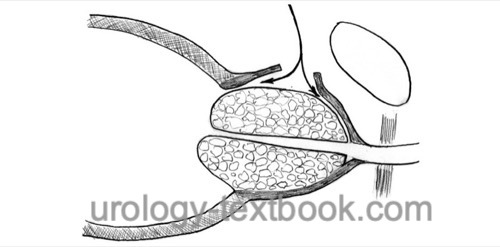
- Incise the mucosa over the lateral lobes, leaving a small strip of the posterior prostatic urethra. Now, both lateral lobes can be bluntly dissected and removed.
- Dissect the median lobe bluntly and incise the overlying mucosa at the bladder neck level before removal.
 |
 |
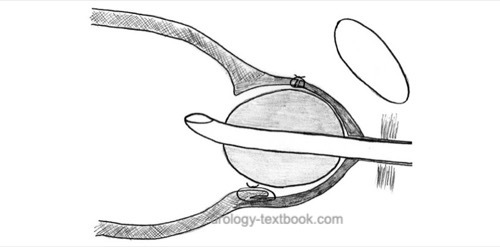 |
Hemostasis after Retropubic Prostatectomy:
- Apply figure-of-eight sutures of the bladder neck at 4 and 8 o'clock positions for significant bleeding (do not incorporate the ureteric orifices).
- Major bleeding should be stopped now; control discrete bleeding with electrocautery or suture ligatures.
- Readvance the irrigation catheter into the bladder and block with 50 ml.
Wound Closure:
- Close the capsulotomy with a running suture (2-0 vicryl).
- Irrigate the wound cavity.
- Insert a wound drainage (e.g., closed gravity system)
- Close the fascia, subcutis, and cutis separately.
Postoperative Care after Retropubic Prostatectomy
General measures: consider patient-controlled analgesia for pain management. Early mobilization and exercises to prevent thrombosis and pneumonia. Thrombosis prophylaxis. Laboratory tests (hemoglobin, creatinine level), regular physical examination of the abdomen, and incision wound.
- After surgery: continuous bladder irrigation. Control excessive bleeding by gentle traction on the catheter. If unsuccessful, proceed with transurethral coagulation of the prostate to control bleeding.
- First day: reduce or stop the continuous irrigation. Patient ambulation.
- Second day: reduce the catheter balloon to 30 ml. Remove the wound drainage (if <75 ml/24 h drainage).
- Third to fifth day: remove the irrigation catheter; consider cystography to ensure a watertight bladder closure of the capsulotomy.
Complications of Retropubic Prostatectomy
- Often retrograde ejaculation (80–90%)
- Bleeding: re-exploration (transurethral coagulation) and blood transfusion are possible.
- Initial urinary incontinence is often due to an overactive bladder. Rarely persistent urinary incontinence due to urinary sphincter damage.
- Rarely persistent Erectile dysfunction
- Urinary tract infections
- Ureteral injury.
- Bladder neck stenosis, urethral stricture
- Surgical site infections
- Urinoma
- Thrombosis, pulmonary embolism
| Greenlight laser | Index | Retropubic radical prostatectomy |
Index: 1–9 A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z
References
J. A. Smith, S. S. Howards, G. M. Preminger, and R. R. Dmochowski, Hinman’s Atlas of Urologic Surgery Revised Reprint. Elsevier, 2019.
 Deutsche Version: transvesikale Adenomektomie
Deutsche Version: transvesikale Adenomektomie
Urology-Textbook.com – Choose the Ad-Free, Professional Resource
This website is designed for physicians and medical professionals. It presents diseases of the genital organs through detailed text and images. Some content may not be suitable for children or sensitive readers. Many illustrations are available exclusively to Steady members. Are you a physician and interested in supporting this project? Join Steady to unlock full access to all images and enjoy an ad-free experience. Try it free for 7 days—no obligation.
New release: The first edition of the Urology Textbook as an e-book—ideal for offline reading and quick reference. With over 1300 pages and hundreds of illustrations, it’s the perfect companion for residents and medical students. After your 7-day trial has ended, you will receive a download link for your exclusive e-book.