You are here: Urology Textbook > Prostate > Prostate cancer > Screening
Prostate Cancer: Screening and Diagnosis
- Prostate cancer: Epidemiology and etiology
- Prostate cancer: Pathology
- Prostate cancer: Signs and symptoms
- Prostate cancer: Screening
- Prostate cancer: Staging
- Prostate cancer: Treatment options
- Prostate cancer: Active surveillance
- Prostate cancer: Prostatectomy
- Prostate cancer: Radiation therapy
- Prostate cancer: Brachytherapy
- Prostate cancer: TURP and experimental treatment options
- Prostate cancer: Hormonal therapy of advanced prostate cancer
- Prostate cancer: Treatment of castration-resistant prostate cancer
Guidelines and review literature: EAU Guidelines Prostate Cancer, (S3-Leitlinie Prostatakarzinom) (Walsh-Campbell Urology 11th Edition).
Recommendations for Prostate Cancer Screening
Prostate cancer screening includes measurement of the prostate-specific antigen concentration (PSA) and digital rectal examination (DRE) in asymptomatic men. If either test is repeatedly suspicious, further examinations are necessary. The proportion of prostate carcinomas detected in screening groups is significantly higher compared to observational groups. The screening also reveals numerous carcinomas that do not require treatment. Prostate cancer-specific mortality is reduced by the screening. An influence on the overall survival time has not been demonstrated. Prostate cancer screening is controversial due to limited evidence to reduce overall mortality. Before screening, men should be given open-ended counseling about the pros and cons, especially the significance of positive and negative test results, overdiagnosis, and any further measures that may be needed (S3 Guideline, 2015)-
Age recommendations for PSA screening:
In general, PSA screening is recommended at the age of 45 years [see figure flowchart prostate cancer screening]. In high-risk patients for prostate cancer (first-degree relatives with prostate cancer, black men), PSA screening should start at 40. The screening test should be performed annually. With low PSA concentrations and inconspicuous DRE, the screening intervals can be extended depending on PSA levels: 1–2 ng/ml every two years and below 1 ng/ml every four years. For men over 70 years and a PSA value below 1 ng/ml, further PSA screening is not recommended.
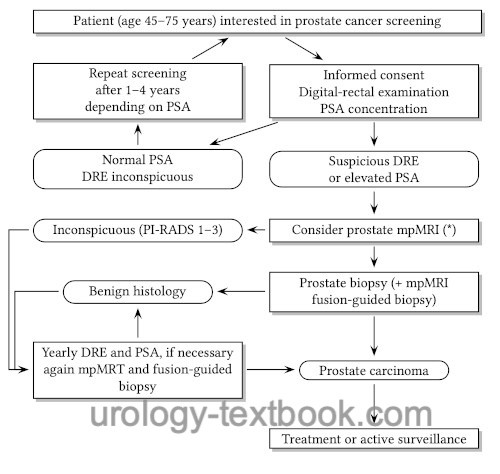 |
Evidence of Prostate Cancer Screening
So far, two large randomized studies have examined the reduction of mortality by prostate cancer screening.
PLCO trial:
Randomized study, 76.693 men, screening with DRE and PSA vs. standard care, follow-up 7 years (Andriole et al., 2009). Number of diagnosed prostate cancer: 2820 vs. 2322. 50 vs. 44 deaths (insignificant). The study is criticized for methodological errors because 90% of patients in the observational group received a PSA test (Shoag et al., NEJM 2016).
ERSPC trial:
Randomized study, 72,952 men were screened with DRE and PSA vs. 89 435 men with standard care (Schröder et al., 2009). Cumulative incidence of prostate cancer after 9 years of follow: 8.2% vs. 4.8%, in absolute numbers 5990 vs. 4307. Relative risk of death from prostate cancer in the screening group was 0.8 (214 vs. 326 deaths due to prostate cancer). If men were excluded due to non-compliance, the relative risk of prostate cancer death in the screening group was 0.7 (Roobol et al., 2009). The relative risk of bone metastases or PSA >100 ng/ml in the screening group was 0,59.
According to the primary results of the ERSPC trial, 1410 men must participate in the screening program (Number needed to screen) to prevent one death due to prostate cancer. Furthermore, 48 men must be treated for prostate cancer (Number needed to treat) to prevent one death due to prostate cancer. With prolonged follow-up, the number needed to screen and treat improve:
| Follow-up in years | Number needed to screen | Number needed to treat |
| 9 | 1410 | 48 |
| 11 | 979 | 35 |
| 13 | 781 | 27 |
Arguments against PSA screening:
Opponents of PSA screening fear an overtreatment of clinically insignificant prostate cancer and refer to epidemiology data and the above-mentioned trials. Although the ERSPC trial showed a reduction in mortality by up to 30% with PSA screening, the reduction is judged to be too low to recommend PSA screening generally.
Risk-adapted PSA screening:
In order to avoid over-diagnosis and over-treatment, a risk calculator was introduced based on the data of the ERSPC trial. With the help of age, LUTS, ethnicity, family history, DRE, prostate volume, and PSA, the risk of a cancer-positive prostate needle biopsy can be estimated. The risk calculator is published on the internet: www.prostatecancer-riskcalculator.com.
Diagnosis of Prostate Cancer
Digital rectal examination (DRE)
DRE for screening
The sensitivity of DRE (probability of suspicious DRE if prostate cancer is present) for localized prostate cancer is low. The specificity of DRE (probability of prostate cancer in suspicious DRE) is also low. Specificity can be improved by consideration of the PSA concentration: specificity for suspicious DRE in white men is 5% (0–1 ng/ml), 14% (1.1 to 2.5 ng/ml), and 29% (2.6 to 4 ng/ml). For black men, the specificity of suspicious DRE is almost twice as high for the same PSA concentration.
DRE and assessment of local tumor stage:
T1 (not palpable), T2 (palpable tumor, organ confined), T3a (tumor extends through the prostatic capsule), T3b (seminal vesicle invasion), T4 (infiltration of neighboring organs such as the rectum or pelvic wall). The accuracy of the DRE for the local tumor stage is low; imaging with MRI is recommended for locally advanced prostate carcinoma.
Prostate-specific antigen (PSA)
PSA is indicated for screening, predicting prognosis for biopsy-proven prostate cancer, and follow-up after curative therapy or metastatic disease. See section laboratory values/PSA.
PSA and screening for prostate cancer:
One gram of benign prostatic hyperplasia increases the PSA concentration by 0.3 ng/ml, while one gram of prostate cancer increases PSA by 3.5 ng/ml. Due to the significant differences in quantities of tissue for BPH (many grams) or prostate cancer (few grams), static normal values are unable to differentiate between prostate cancer and BPH.
Reference values of PSA
It is not wise to initiate a prostate biopsy for a fixed reference value (e.g., 4 ng/ml). The prediction accuracy of the PSA would be too low, many prostate biopsies would yield benign hyperplasia as a result, and some prostate cancer might be overlooked. The prediction accuracy of PSA can be improved by considering age-related reference values, the yearly increase (PSA velocity), and the concentration of free PSA (fPSA). Suspekt for carcinoma are PSA levels above 2.5 ng/ml, a PSA velocity above 0.75 ng/ml/year, and fPSA values below 20% [EAU Guidelines]. An elevated PSA level should be controlled for confounding factors and repeated.
In addition, the PSA concentration must be interpreted in relation to other clinical variables (DRE, age, family history, imaging). This reduces unnecessary prostate biopsies and improves the detection of prostate carcinoma [Table PSA, DRE and prostate carcinoma risk]. But there is also a risk for prostate carcinoma even within the normal range of the PSA concentration [Table Normal PSA values and prostate carcinoma risk].
| DRU | PSA (ng/ml) | Risk for PCA |
| not suspicious | 0–4 | 4–9 % |
| not suspicious | >4 | 12–32 % |
| suspicious | 0–4 | 13–21 % |
| suspicious | >4 | 42–72 % |
| PSA (ng/ml) | Risk for PCA | Risk for Gleason ≥7 |
| <0,5 | 7 % | 0,8 % |
| 0,6–1,0 | 10 % | 1 % |
| 1,1–2,0 | 17 % | 2 % |
| 2,1–3,0 | 24 % | 5 % |
| 3,1–4,0 | 27 % | 7 % |
Transrectal Ultrasound of the Prostate (TRUS)
Transrectal ultrasound probes use 4 to 10 MHz transducers with transverse and sagittal image construction. Prostate cancer foci present as hypoechoic areas but are often invisible (isoechoic) or hyperechoic [fig. advanced prostate cancer in TRUS]. Prostate cancers, visible in TRUS as hypoechoic areas, have a larger tumor volume, a higher Gleason score and a worse prognosis than non-visible carcinomas (Amiel and Slavin, 2006). However, transrectal sonography is not reliable enough to screen localized prostate carcinoma. Modern ultrasound methods have been developed to improve the visibility of prostate cancer (elastography or histoscanning), but they have not proven reliable enough in controlled trials; please see the section on experimental prostate cancer diagnosis.
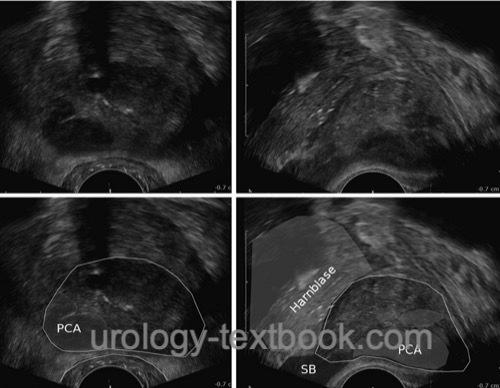 |
Multiparametric MRI of the prostate
Multiparametric MRI (mpMRI) is used to localize intraprostatic tumor growth and to assess the local tumor stage. A prerequisite for a high-quality mpMRT is using 1.5 or 3 Tesla scanners. The mpMRT uses different examination sequences such as T1- and T2-weighting, diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI), 1H-MR spectroscopy, and dynamic contrast-enhanced MRI (dceMRI); please see table examination sequences of mpMRI of the Prostate and fig. mpMRT of prostate cancer.
| Abbreviation | Description | Diagnostic information |
| T1 | Spin–lattice relaxation time | The physiological signal intensity of the prostate in T1 imaging is low. |
| T2 | Spin–spin relaxation time | The normal peripheral zone has a high homogeneous signal in T2 imaging, and the small prostatic capsule presents with lower signal intensity. Prostate cancer foci usually present with a lower signal intensity. |
| DWI | Diffusion-weighted imaging | Imaging correlates with the Brownian motion of water molecules between the cells. In the case of prostate cancer, the signal of DWI imaging is lower due to a higher cell density. |
| 1H-MRS | Proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy | Provides metabolic information from citrate methylene protons (Cit) and the methyl groups of creatine (Cr)- and choline (Cho)-containing compounds. |
| dceMRI | Dynamic contrast-enhanced MRI | Repeated T1-weighted imaging after applying contrast medium provides information about the blood vessel quantity, blood flow and capillary permeability. |
| Do you want to see the illustration? Please support this website with a Steady membership. In return, you will get access to all images and eliminate the advertisements. Please note: some medical illustrations in urology can be disturbing, shocking, or disgusting for non-specialists. Click here for more information. |
| Do you want to see the illustration? Please support this website with a Steady membership. In return, you will get access to all images and eliminate the advertisements. Please note: some medical illustrations in urology can be disturbing, shocking, or disgusting for non-specialists. Click here for more information. |
| Do you want to see the illustration? Please support this website with a Steady membership. In return, you will get access to all images and eliminate the advertisements. Please note: some medical illustrations in urology can be disturbing, shocking, or disgusting for non-specialists. Click here for more information. |
| Do you want to see the illustration? Please support this website with a Steady membership. In return, you will get access to all images and eliminate the advertisements. Please note: some medical illustrations in urology can be disturbing, shocking, or disgusting for non-specialists. Click here for more information. |
| Do you want to see the illustration? Please support this website with a Steady membership. In return, you will get access to all images and eliminate the advertisements. Please note: some medical illustrations in urology can be disturbing, shocking, or disgusting for non-specialists. Click here for more information. |
| Do you want to see the illustration? Please support this website with a Steady membership. In return, you will get access to all images and eliminate the advertisements. Please note: some medical illustrations in urology can be disturbing, shocking, or disgusting for non-specialists. Click here for more information. |
Indications for mpMRI:
Performing mpMRI before a prostate biopsy offers several advantages: suspicious areas on imaging can be targeted for biopsy, and patients with unremarkable imaging can omit prostate biopsy (depending on the PSA). In the current EAU guidelines (as of 2020), mpMRI is recommended before the first prostate biopsy; the German S3 guideline is more cautious and suggests mpMRI as an option. According to current data, the sensitivity is 85–90% to exclude significant prostate carcinoma. A prostate biopsy should still be recommended if clinical suspicion is high and imaging is unremarkable.
All current guidelines recommend mpMRI after a negative prostate biopsy and persistent suspicion of prostate cancer. If imaging is unremarkable, a further prostate biopsy is unnecessary, or a targeted biopsy is possible for suspicious lesions.
Locally advanced prostate carcinoma is also an indication for mpMRI, and the pelvic lymph nodes should also be assessed.
The importance of mpMRI during active surveillance has not yet been adequately studied, but promises to be a good follow-up parameter. Current guidelines recommend mpMRI based biopsy for treatment decision regarding active surveillance and for any further follow-up biopsy.
PI-RADS Classification:
In 2012, the European Society of Urogenital Radiology (ESUR) published a guideline, updated in 2014, to improve and standardize the technique and interpretation of mpMRI [table PI-RADS classification for mpMRI]. PI-RADS stands for Prostate Imaging Reporting and Data System. The higher the PI-RADS score of a lesion, the more likely is the presence of a significant prostate carcinoma.
| PI-RADS Score | Probability of significant prostate cancer |
| 1 | most probably benign |
| 2 | probably benign |
| 3 | indeterminate (15%) |
| 4 | probably malignant (27%), Läsion <1,5 cm |
| 5 | highly suspicious of malignancy (88%), Läsion >1,5 cm |
The reporting of the lesion localization is also standardized: the prostate is divided in right and left, anterior/posterior, and the apex/middle/base. The lesions are additionally assigned to the prostate zones: peripheral zone, transition zone, central zone, or anterior fibromuscular stroma.
Prostate needle biopsy
Indications for prostate biopsy:
A suspicious DRE and an elevated/rising PSA concentration are indications for a prostate biopsy. The prediction accuracy of PSA can be improved by considering age-related reference values, the yearly increase (PSA velocity), and the concentration of free PSA (fPSA), see above. If in doubt, a multiparametric prostate MRI can help decide for or against a prostate biopsy. At a certain age, localized prostate carcinoma does not influence life expectancy, so prostate biopsy should be indicated regarding life expectancy, PSA concentration, and symptoms.
Negative prostate biopsy and elevated PSA:
In the case of persisting clinical suspicion for prostate carcinoma, the prostate biopsy should be repeated, possibly with an increased number of biopsy cores, and after performing a mpMRI to enable targeted biopsy. The second biopsy can be delayed for at least six months without any worries about tumor progression. The results of the European Screening Study show that small tumors are missed by the first biopsy.
Technique of prostate biopsy:
Outdated standard is the transrectal ultrasound-guided prostate biopsy. To avoid infection, perineal prostate biopsy should be offered as a new standard. At least 10 biopsy cores are taken from the peripheral zone of the prostate. If an mpMRI of the prostate is available, fusion biopsy of the prostate is possible, see section surgical technique of prostate biopsy.
Pathological interpretation of prostate biopsy:
See section prostate cancer/pathology for interpretation.
| prostate cancer symptoms | Index | prostate cancer staging |
Index: 1–9 A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z
References
Amiel und Slawin 2006 AMIEL, Gilad E. ; SLAWIN, Kevin M.: Newer modalities of ultrasound imaging and treatment of the prostate.In: Urol Clin North Am
33 (2006), Aug, Nr. 3, S. 329–337.
G. L. Andriole, R. L. Grubb, S. S. B. et. al., and the PLCO Project Team. Mortality results from a randomized prostate-cancer screening trial.
N Engl J Med, Mar 2009. Cooner u.a. 1990 COONER, W. H. ; MOSLEY, B. R. ; RUTHERFORD, Jr. ; BEARD, J. H. ; POND, H. S. ; TERRY, W. J. ; IGEL, T. C. ; KIDD, D. D.: Prostate cancer detection in a clinical urological practice by ultrasonography, digital rectal examination and prostate-specific antigen.
In: J Urol
143 (1990), Nr. 6, S. 1146–52; discussion 1152–4
Crawford, E. D.; Grubb, 3rd, R.; Black, A.; Andriole, Jr, G. L.; Chen, M.-H.; Izmirlian, G.; Berg, C. D. & D'Amico, A. V. Comorbidity and mortality results from a randomized prostate cancer screening trial.
J. Clin. Oncol. 2011, 29, 355-361.
DeMarzo u.a. 2003 DEMARZO, A. M. ; NELSON,
W. G. ; ISAACS, W. B. ; EPSTEIN, J. I.:
Pathological and molecular aspects of prostate cancer.
In: Lancet
361 (2003), Nr. 9361, S. 955–64N. Mottet (Chair), J. Bellmunt, E. Briers (Patient Representative), R.C.N. van den Bergh (Guidelines Associate),
M. Bolla, N.J. van Casteren (Guidelines Associate), P. Cornford, S. Culine, S. Joniau, T. Lam, M.D. Mason, V. Matveev, H. van der Poel, T.H. van der Kwast, O. Rouvière, T. Wiegel
Guidelines on Prostate Cancer of the European Association of Urology (EAU), https://uroweb.org/guidelines/prostate-cancer/.
Leitlinienprogramm Onkologie (Deutsche Krebsgesellschaft, Deutsche Krebshilfe,
AWMF):
Interdisziplinäre Leitlinie der Qualität S3 zur Früherkennung, Diagnose und Therapie der verschiedenen Stadien des Prostatakarzinoms, Langversion 3.1, 2014 AWMF Registernummer: 034/022OL, https://www.awmf.org//leitlinien/detail/ll/043-022OL.html (Zugriff am: 07.02.2016)
Ellis u.a. 1994 ELLIS, W. J. ; CHETNER,
M. P. ; PRESTON, S. D. ; BRAWER, M. K.:
Diagnosis of prostatic carcinoma: the yield of serum prostate
specific antigen, digital rectal examination and transrectal ultrasonography.
In: J Urol
152 (1994), Nr. 5 Pt 1, S. 1520–5
Pound u.a. 1999 POUND, C. R. ; PARTIN, A. W. ;
EISENBERGER, M. A. ; CHAN, D. W. ; PEARSON,
J. D. ; WALSH, P. C.:
Natural history of progression after PSA elevation following radical
prostatectomy.
In: Jama
281 (1999), Nr. 17, S. 1591–7
Roobol, M. J.; Kerkhof, M.; Schröder, F. H.; u.a.m. Prostate cancer mortality reduction by prostate-specific antigen-based screening adjusted for nonattendance and contamination in the European Randomised Study of Screening for Prostate Cancer (ERSPC).
Eur. Urol. 2009, 56, 584-591.
Wein, A. J.; Kavoussi, L. R.; Partin, A. P. & Peters, C. A. Campbell-Walsh Urology
. Elsevier, 2015. ISBN 978-1455775675.
 Deutsche Version: Früherkennung des Prostatakarzinoms
Deutsche Version: Früherkennung des Prostatakarzinoms