You are here: Urology Textbook > Drugs in Urology > Alpha blocker > Doxazosin
Doxazosin: Mechanism, Adverse Effects and Dosage
- Alpha blockers: General pharmacology
- Alpha blocker Alfuzosin
- Alpha blocker Doxazosin
- Alpha blocker Silodosin
- Alpha blocker Tamsulosin
- Alpha blocker Terazosin
Mechanism of Action
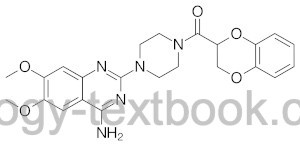
Doxazosin is a nonselective α1-blocker with long elimination half-life. Please see section general pharmacology of alpha blocker.
 |
Indications for Doxazosin
- Treatment of benign prostatic hyperplasia: Doxazosin improves urinary flow and bladder emptying, relieves irritative and obstructive urinary symptoms (LUTS), reduces the risk of urinary retention, improves the success of a trial without a catheter after urinary retention, and is approved for long-term use.
- Treatment of arterial hypertension as a second-line add-on in patients with insufficient effect of the first-line medication.
- Off-label treatment of female LUTS due to neurogenic bladder neck obstruction.
- Off-label treatment: improve the spontaneous passage of distal ureteral stones.
Pharmacokinetics of Doxazosin
- Well absorbed after oral administration, bioavailability 65%, high protein binding, hepatic metabolism (CYP3A4).
- Elimination half-life 22 hours, time to steady-state seven days.
Adverse Effects of Doxazosin
Increased side effect profile since doxazosin is a nonselective α1 blocker.
- Hypotension, orthostatic syncope, reflex tachycardia
- Stuffy nose
- Retrograde ejaculation
- Tachyphylaxis in the treatment of hypertension due to volume retention and peripheral edema.
- Dizziness, weakness
- Rare side effects: priapism (alpha blocker inhibit sympathetic mechanisms for detumescence), intraoperative floppy iris syndrome during cataract surgery.
Contraindications of Doxazosin
Urological Contraindications:
Conservative treatment of BPH with doxazosin is not indicated, if surgical treatment is imperative: chronic urinary retention with renal failure, recurrent hematuria due to prostatic enlargement, recurrent urinary tract infections and bladder stones.
Cardiac Contraindications:
Hypotension, mechanical heart failure (valvular diseases, pulmonary embolism, pericarditis), congestive heart failure.
Other contraindications:
Doxazosin should be paused for cataract surgery to prevent an intraoperative floppy iris syndrome.
Drug interactions
- Increased hypotensive effect with other antihypertensives or phosphodiesterase-5 inhibitors.
- CYP3A4 inhibitors such as ketoconazole increase the terazosin plasma level and side effects.
- Do not combine doxazosin with another alpha blocker for better treatment effect.
Dosage of Doxazosin
The treatment of doxazosin should be started with a low dosage, such as 1 mg orally once daily. The dosage can be increased each week to 2–4–8 mg orally once daily, depending on treatment effect, side effects and blood pressure. Doxazosin should be given before bedtime in the evening to reduce side effects.
| Terazosin | Index | Tamsulosin |
Index: 1–9 A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z
References
Chapple 2004 CHAPPLE, C. R.:
Pharmacological therapy of benign prostatic hyperplasia/lower urinary
tract symptoms: an overview for the practising clinician.
In: BJU Int
94 (2004), Nr. 5, S. 738–44
Fusco et al., “Alpha-Blockers Improve Benign Prostatic Obstruction in Men with Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis of Urodynamic Studies.,” Eur Urol., vol. 69, no. 6, pp. 1091–1101, 2016, doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2015.12.034.
J. D. McConnell et al., “The long-term effect of doxazosin, finasteride, and combination therapy on the clinical progression of benign prostatic hyperplasia,” N Engl J Med, vol. 349, no. 25, pp. 2387–98, 2003.
C. de Mey, “alpha(1)-blockers for BPH: are there differences?,” Eur Urol, vol. 36 Suppl 3, pp. 52–63, 1999.
 Deutsche Version: Doxazosin
Deutsche Version: Doxazosin
Urology-Textbook.com – Choose the Ad-Free, Professional Resource
This website is designed for physicians and medical professionals. It presents diseases of the genital organs through detailed text and images. Some content may not be suitable for children or sensitive readers. Many illustrations are available exclusively to Steady members. Are you a physician and interested in supporting this project? Join Steady to unlock full access to all images and enjoy an ad-free experience. Try it free for 7 days—no obligation.
New release: The first edition of the Urology Textbook as an e-book—ideal for offline reading and quick reference. With over 1300 pages and hundreds of illustrations, it’s the perfect companion for residents and medical students. After your 7-day trial has ended, you will receive a download link for your exclusive e-book.