You are here: Urology Textbook > Kidneys > Kidney infarction
Kidney Infarction
Definition of Renal Artery Embolism and Kidney Infarction
Renal artery embolism leads to a sudden interruption of blood flow in the renal artery or its main segmental branches and ischemic kidney infarction. A hemorrhagic renal infarction can be the result of a renal vein thrombosis.
Epidemiology:
Renal infarction is a common autopsy finding in 1%, but rare diagnosed in patients (0,02/1000 emergency department patients) (Lopez et al., 2010).
Etiology (Causes) of Kidney Infarction
- Thromboembolic event (90%). Risk factors are atrial fibrillation, mitral valve disease, coronary heart disease, heart failure, other heart diseases, cardiac surgery, aortic aneurysm, renal artery aneurysm, or renal artery stenosis.
- Hemorrhagic renal infarction due to renal vein thrombosis
Pathology:
Embolism of the renal artery branches leads to a wedge-shaped anemic infarct with a hemorrhagic rim. Thrombosis of the renal vein leads to a hemorrhagic infarction.
Signs and Symptoms
Most renal infarcts are not recognized as such, and the symptoms are mismatched:
- Flank pain or abdominal pain
- Hematuria
- Arterial hypertension
- Irregular heart rate
- Nausea, vomiting
- Oliguria, Anuria
Diagnostic Workup
Urine:
Proteinuria, microhematuria or hematuria.
Laboratory tests:
Signs for kidney infarction are increased GOT, LDH, CK (intracellular enzymes indicating necrosis), and creatinine (if significant renal tissue is affected).
Ultrasonography:
Doppler ultrasonography of the kidney can quickly confirm the diagnosis of complete kidney infarction. After healing of segmental renal infarction, the affected region shrinks and a deep-drawn scar remains visible.
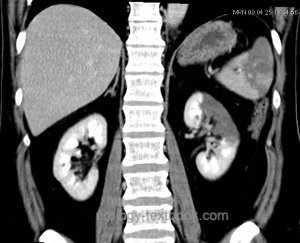
Abdominal CT:
Easy diagnosis in contrast CT scan with wedge-shaped areas without contrast enhancement [fig. partial renal infarction]. The cortical rim sign is seen in 50% of the patients after several hours or days of infarction: a thin rim of cortex enhances due to collateral capsular perfusion.
 |
Digital subtraction angiography (DSA):
The gold standard for diagnosis of acute vascular occlusion with the option for invasive treatment.
Treatment of Kidney Infarction
Conservative Treatment of Kidney Infarction:
Cornerstones of conservative treatment are analgesics, regulation of blood pressure, and systemic heparinization. A thrombolytic therapy should be considered; the decision depends on the extent of infarction and the remaining renal function.
PTA or Surgical Therapy:
Percutaneous transluminal angioplasty or vascular surgery are indicated for patients with bilateral embolism or infarction of a solitary kidney if the diagnosis is made in time. The time window for successful interventions is unclear, the procedures have to be done as an emergency. Please see anatomic or extra-anatomic bypass surgery ( treatment of renal artery stenosis).
| Urologic Surgery | Index | Renal AV fistula |
Index: 1–9 A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z
References
V. M. Lopez and J. Glauser, “A case of renal artery thrombosis with renal infarction.,” J Emerg Trauma Shock, vol. 3, no. 3, p. 302, 2010.
 Deutsche Version: Niereninfarkt
Deutsche Version: Niereninfarkt
Urology-Textbook.com – Choose the Ad-Free, Professional Resource
This website is designed for physicians and medical professionals. It presents diseases of the genital organs through detailed text and images. Some content may not be suitable for children or sensitive readers. Many illustrations are available exclusively to Steady members. Are you a physician and interested in supporting this project? Join Steady to unlock full access to all images and enjoy an ad-free experience. Try it free for 7 days—no obligation.
New release: The first edition of the Urology Textbook as an e-book—ideal for offline reading and quick reference. With over 1300 pages and hundreds of illustrations, it’s the perfect companion for residents and medical students. After your 7-day trial has ended, you will receive a download link for your exclusive e-book.