You are here: Urology Textbook > Penis > Penile fracture
Penile Fracture: Causes, Diagnosis and Treatment of Cavernosal Rupture
Definition
Penile fracture is the rupture of the corpora caverosa during erection due to bending trauma (Sawh et al., 2008) EAU Guidelines: Urological Trauma.
Epidemiology of Penile Fracture
Infrequent, 1 of 175.000 hospital admissions.
Etiology of Penile Fracture
A penile fracture usually arises from a bending trauma during vigorous sexual intercourse, especially when the penis slips out of the vagina. Furthermore, penile fractures are caused by masturbation practices with bending of the penile shaft during erection (practice of taghaandan).
Signs and Symptoms
Patients report a traumatic bending of the erect penis, often with a cracking noise. Typically, a sudden detumescence occurs and a massive penile hematoma develops [fig. clinical presentation of penile fracture]. A defect in the tunica albuginea may be palpable, and the penis bends to the non-ruptured side. Bloody discharge from the urethra is a sign of concomitant urethral injury.
Complications of Penile Fracture
Untreated penile fracture may lead to penile deviation, erectile dysfunction and urethral stricture.
Diagnosis of Penile Fracture
When patients present the typical signs and symptoms, surgical exposure of the penile shaft is justified without further diagnostic workup. When the diagnosis is uncertain, the following imaging studies are recommended.
Penile Ultrasound Imaging
Penile ultrasound imaging with a 10 MHz transducer may show the defect of the tunica albuginea [fig. ultrasound imaging of a penile fracture]. It is not reliable enough for the exclusion of the diagnosis.
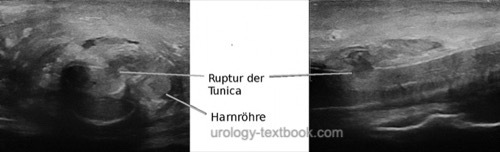 |
Cavernosography:
Cavernosography of the penis can reliably exclude a penile fracture in doubtful cases. Cavernosography is unnecessary with typical signs and symptoms.
MRI:
Magnetic resonance imaging can reliably demonstrate the localization of the penis fracture or exclude the diagnosis [fig. MRI imaging of a penile fracture].
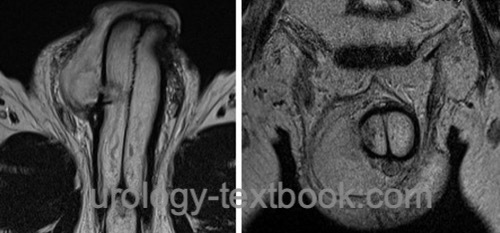 |
Differential Diagnosis of Penile Fracture
Penile injury with subcutaneous bleeding can be confused with a penile fracture.
Treatment of penile fracture
Surgical Treatment of Penile Fracture
Emergency surgery is unnecessary since elective operations have equally good results (el-Assmy et al., 2011). A urethral catheter is inserted before the operation. A circumcising incision is used to approach the penile shaft if the location of the rupture is uncertain. Alternatively, a direct approach to the fracture location is possible. The tunica albuginea is sutured with absorbable sutures (2-0 or 3-0). Care is taken to identify and suture a urethral injury. A circular dressing prevents further swelling after skin closure.
Care after surgical therapy: remove drains and catheter after 1–2 days. The catheter should be left for 3–7 days depending on the severity of a urethral injury. No sexuell activity for 6–8 weeks, but after two weeks gentle stretching and manipulation to prevent adhesions is allowed.
Conservative Management of Penile Fracture
Initial bed rest, antiandrogens (or benzodiazepines) against erections, cooling of the penis, and circular dressings are the mainstones of conservative therapy. Conservative treatment leads to more complications than surgical therapy: penile deviation, penile pain, massive hematomas, persistent swelling and diverticula of the penile corpora.
Prophylactic antibiotics
Prophylactic antibiotics are recommended in surgical and conservative therapy of the penile fracture.
| Penile injury | Index | Balanitis |
Index: 1–9 A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z
References
EAU Guidelines: Urological Trauma
el-Assmy, Ahmed; el-Tholoth, Hossam S; Mohsen, Tarek &
el-Housseiny I Ibrahiem
Does timing of presentation of penile fracture
affect outcome of surgical intervention?
Urology, 2011,
77, 1388-1391.
Sawh, S. L.; O'Leary, M. P.; Ferreira, M. D.; Berry, A.
M. & Maharaj, D.
Fractured penis: a review.
Int J Impot Res, 2008,
20, 366-369.
 Deutsche Version: Penisfraktur
Deutsche Version: Penisfraktur