You are here: Urology Textbook > Kidneys > Parapelvic cysts
Parapelvic Cysts of the Kidney: Symptoms, Diagnosis and Treatment
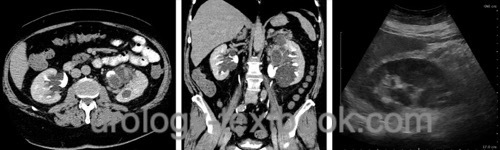
Definition of Renal Parapelvic Cysts
Parapelvic cysts of the kidneys are simple renal cysts adjacent to the renal pelvis or the renal sinus.
 |
Etiology of Parapelvic Cysts
Typical parapelvic cysts are multiple and probably derive from lymphatic vessels, often associated with nephrolithiasis or urinary obstruction. Parapelvic cysts may also derive from the renal parenchyma adjacent to the renal pelvis.
Signs and Symptoms
Usually, there are no complaints. Parapelvic cysts can compress the pyelocalyceal system or ureter, cause flank pain, or lead to other symptoms of urinary obstruction.
Diagnostic Workup of Parapelvin Cysts
Renal ultrasound should be sufficient in most cases for the diagnosis. In doubtful ultrasound findings, perform an intravenous pyelography, abdominal CT, or renal scintigraphy to rule out a urinary obstruction.
Differential Diagnosis of Parapelvic Cysts
Hydronephrosis (upper urinary tract obstruction).
Treatment of Parapelvic Cysts
Treatment of parapelvic cysts is rarely necessary; see section simple renal cyst.
| Kidney cysts | Index | Renal diseases |
Index: 1–9 A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z
References
Israel, G. M. & Bosniak, M. A.
An update of the Bosniak renal cyst classification system.
Urology, 2005, 66, 484-488
 Deutsche Version: Parapelvine Nierenzyste
Deutsche Version: Parapelvine Nierenzyste
Urology-Textbook.com – Choose the Ad-Free, Professional Resource
This website is designed for physicians and medical professionals. It presents diseases of the genital organs through detailed text and images. Some content may not be suitable for children or sensitive readers. Many illustrations are available exclusively to Steady members. Are you a physician and interested in supporting this project? Join Steady to unlock full access to all images and enjoy an ad-free experience. Try it free for 7 days—no obligation.
New release: The first edition of the Urology Textbook as an e-book—ideal for offline reading and quick reference. With over 1300 pages and hundreds of illustrations, it’s the perfect companion for residents and medical students. After your 7-day trial has ended, you will receive a download link for your exclusive e-book.