You are here: Urology Textbook > Testes > Torsion of testicular appendage
Torsion of Testicular Appendage – Hydatid Torsion
Definition
Torsion of Testicular Appendage is the rotation of the testicular appendix (hydatid of Morgagni) around its pedicle, leading to hemorrhagic necrosis.
Signs and Symptoms of Hydatid Torsion
- Testicular pain
- Edema of the scrotum
- Blue dot sign: the hemorrhagic infarcted appendix testis is visible through the scrotum
Diagnostic Workup
Imaging
Doppler ultrasonography of the testis: signs for torsion of testicular appendage are a mild hydrocele and an enlarged testicular appendix [fig. ultrasonography of hydatid torsion ] and evidence of testicular blood flow. The reliable differentiation between testicular torsion and torsion of the testicular appendage can be difficult; surgical exploration may be necessary.
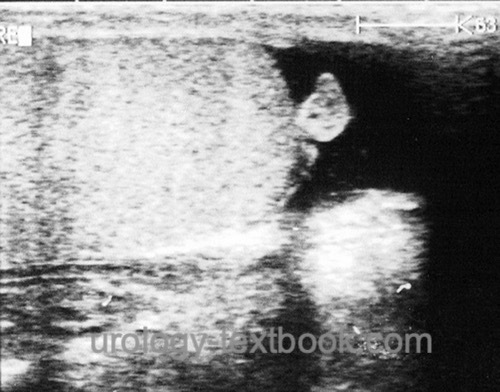 |
Ultrasonography of hydatid torsion: with hydrocele and a visible testicular appendix. With kind permission, Prof. Dr. R. Harzmann, Augsburg. |
Treatment of Hydatid torsion
In principle, the torsion of testicular appendage is treated conservatively with analgesics. In the case of surgical exploration, the testicular appendage is removed after coagulation of the basis.
| Testicular torsion | Index | Varicocele |
Index: 1–9 A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z
References
C. Radmayr, G. Bogaert, H. S. Dogan, and S. Tekgül, “EAU Guidelines: Paediatric Urology.” [Online]. Available: https://uroweb.org/guidelines/paediatric-urology/
 Deutsche Version: Hydatidentorsion
Deutsche Version: Hydatidentorsion