You are here: Urology Textbook > Testes > Orchitis
Causes, Diagnosis and Treatment of Orchitis
Definition of Orchitis
Acute orchitis is an inflammation of the testicular parenchyma of various causes with swelling and pain. Chronic orchitis is an inflammation of the testicular parenchyma that lasts longer than six weeks.
Epidemiology:
The true incidence of orchitis is unclear, but it is much less common than epididymitis. Common is the inflammation of the testis due to acute epididymitis (epididymoorchitis). Isolated orchitis (without epididymitis) is rare and usually caused by viruses.
Etiology and Differential Diagnosis of Orchitis
- Bakterial epididymoorchitis: local spread of bacterial epididymitis.
- Septic spread of bacterial diseases (Syphilis, typhoid fever, brucellosis, urogenital tuberculosis).
- Viral infections (mumps, infectious mononucleosis).
- Parasites: Malaria, lymphatic filariasis.
- Autoimmune orchitis in vasculitis
Signs and symptoms of Orchitis
Typical are redness, pain, and swelling of the affected scrotal compartment and testis, in addition to the symptoms of the underlying disease.
Diagnosis or Orchitis
- Urine analysis and blood tests depend on the medical history and suspected etiology.
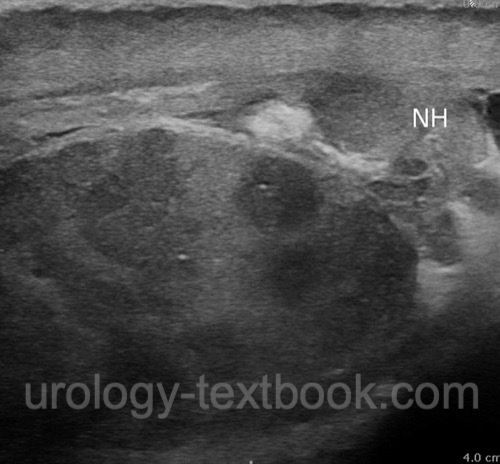
- Testicular ultrasound imaging with Doppler.
- Surgical exploration is necessary if testicular torsion or tumor cannot be excluded.
 |
Treatment of Orchitis
General measures are bed rest, scrotal elevation and cooling, and anti-inflammatory drugs such as diclofenac. Further specific therapy depends on the suspected disease; a calculated antibiotic therapy with fluoroquinolones or cephalosporins is often begun until further laboratory results are available.
Diagnosis and Treatment of Mumps Orchitis
Definition of Mumps Orchitis
Mumps orchitis is an acute viral orchitis and a complication of epidemic parotitis.
Epidemiology
Mumps orchitis develops in 30% of patients with mumps after puberty, and 10–30% have bilateral manifestations.
Etiology and Pathogenesis of Mumps Orchitis
The mumps virus is a neurotropic paramyxovirus with single-stranded RNA. Orchitis leads to infiltration of lymphocytes, damage to the blood-testis barrier, and edema with the rise of intratesticular pressure with pressure atrophy (caused by the inelastic tunica albuginea). Infertility, subfertility, and hypogonadism may develop depending on the extent of the (bilateral) disease.
Signs and Symptoms of Mumps Orchitis
- Incubation period: 14–25 days
- Fever, headache
- parotid inflammation (more common bilateral), cloudy saliva
- Orchitis: the scrotal symptoms occur after 4–6 days with a painful testicular swelling, in 10–30% bilateral.
- Spontaneous improvement of symptoms after 1–2 weeks
Diagnosis
See the section "Diagnosis of orchitis" above.
Treatment of Mumps Orchitis
General measures include bed rest, scrotal elevation, cooling, NSAR or glucocorticoids. In doubtful situations, calculated antibiotic therapy with fluoroquinolones or cephalosporins is begun until further laboratory results are available. Interferon-α (Ku et al., 1999) was successfully used to treat mumps orchitis and to prevent testicular atrophy. However, this is not the standard of care.
Treatment of Infertility after Mumps Orchitis
In the case of azoospermia, recommend testicular sperm extraction (TESE) and ICSI.
Prognosis of Mumps Orchitis
Bilateral orchitis may cause testicular atrophy with infertility, in severe cases with hypergonadotropic hypogonadism.
| Epididymitis | Index | Testicular diseases |
Index: 1–9 A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z
References
Ku, J. H.; Kim, Y. H.; Jeon, Y. S. & Lee, N. K.
The preventive effect of systemic treatment with interferon-alpha2B for
infertility from mumps orchitis.
BJU Int, 1999, 84, 839-842.
Manson 1990 MANSON, A. L.:
Mumps orchitis.
In: Urology
36 (1990), Nr. 4, S. 355–8
M. Masarani, H. Wazait, and M. Dinneen, “Mumps orchitis.,” J R Soc Med, vol. 99, no. 11, pp. 573–575, 2006, doi: 10.1258/jrsm.99.11.573.
 Deutsche Version: Mumps Orchitis
Deutsche Version: Mumps Orchitis
Urology-Textbook.com – Choose the Ad-Free, Professional Resource
This website is designed for physicians and medical professionals. It presents diseases of the genital organs through detailed text and images. Some content may not be suitable for children or sensitive readers. Many illustrations are available exclusively to Steady members. Are you a physician and interested in supporting this project? Join Steady to unlock full access to all images and enjoy an ad-free experience. Try it free for 7 days—no obligation.
New release: The first edition of the Urology Textbook as an e-book—ideal for offline reading and quick reference. With over 1300 pages and hundreds of illustrations, it’s the perfect companion for residents and medical students. After your 7-day trial has ended, you will receive a download link for your exclusive e-book.