You are here: Urology Textbook > Testes > Disorders of sex development > Klinefelter syndrome
Klinefelter Syndrome: Karyotype, Diagnosis and Treatment
Definition of Klinefelter Syndrome
Klinefelter syndrome is the most common sex chromosome disorder and results in primary hypogonadism and infertility in men. The syndrome is caused by an additional X chromosome resulting in a karyotype of 47,XXY. Synonyms: XXY syndrome, 47,XXY males.
Epidemiology of Klinefelter Syndrome
The prevalence is 1:500–1000 in live male births, less than 50% of affected patients are diagnosed.
Karyotype and Pathology of Klinefelter Syndrome
The karyotype of Klinefelter syndrome is 47,XXY. A mosaic karyotype 46,XY/47,XXY is also possible. The cause of the sex chromosome disorder is a defect of meiosis during gametogenesis; meiotic defects of the zygote cause Klinefelter syndromes with mosaic karyotype.
Klinefelter syndrome results in a sclerosis of the seminiferous tubules, missing or severely damaged spermatogenesis, and hyperplasia of Leydig cells. The exact mechanism of hypogonadism is unclear, given the Leydig cell hyperplasia.
Signs and Symptoms
- Male phenotype
- Before puberty, small testes and disproportionately long legs are present. The verbal IQ might be reduced.
- After puberty, signs of androgen deficiency develop (infertility, decreased virilization, small penis, low muscle mass, small firm testes, and gynecomastia). In addition, there is an increased body length (75th percentile in average).
- Untreated adults develop osteoporosis; they have an increased risk of diabetes mellitus, varicosis, breast cancer, lung disease and extragonadal germ cell tumors.
Diagnostic Workup in Klinefelter Syndrome
Klinefelter syndrome should be suspected if azoospermia, hypergonadotropic hypogonadism (increased FSH, low testosterone), and the phenotype mentioned above are present. Karyotyping confirms the diagnosis.
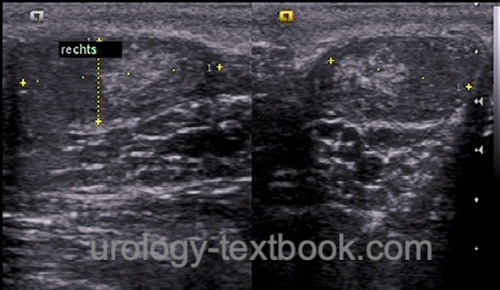
Testicular ultrasound imaging: inhomogeneous nodular echo pattern with testicular microlithiasis, the testicular volume is about 2–3 ml per side. Doppler ultrasound shows high vascular resistance with a high RI (Ekerhovd et al., 2002).
 |
Treatment of Klinefelter Syndrome
Testosterone substitution with the onset of puberty promotes secondary male sex characteristics, reduces gynecomastia, and prevents osteoporosis.
Treatment of infertility:
Infertility can be treated rarely by TESE and ICSI if spermatozoa can be identified in the testicular tissue. The chances are better in younger patients and prior to testosterone substitution (Fullerton et al., 2010). The use of reproductive techniques in adolescents is controversial.
| Persistent Mullerian duct syndrome | Index | 46,XX male syndrome |
Index: 1–9 A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z
References
Ekerhovd, E. & Westlander, G.
Testicular
sonography in men with Klinefelter syndrome shows irregular echogenicity
and blood flow of high resistance.
Journal of assisted reproduction
and genetics, 2002, 19, 517-522.
Fullerton, G.; Hamilton, M. & Maheshwari, A.
Should non-mosaic Klinefelter syndrome men be labelled as infertile in 2009?
Hum
Reprod, 2010, 25, 588-597
A. Salonia, S. Minhas, and C. Bettocchi, “EAU Guidelines: Sexual and Reproductive Health,” 2022. [Online]. Available: https://uroweb.org/guidelines/sexual-and-reproductive-health/.
Lanfranco u.a. 2004 LANFRANCO, F. ; KAMISCHKE,
A. ; ZITZMANN, M. ; NIESCHLAG, E.:
Klinefelter’s syndrome.
In: Lancet
364 (2004), Nr. 9430, S. 273–83
 Deutsche Version: Klinefelter-Syndrom
Deutsche Version: Klinefelter-Syndrom
Urology-Textbook.com – Choose the Ad-Free, Professional Resource
This website is designed for physicians and medical professionals. It presents diseases of the genital organs through detailed text and images. Some content may not be suitable for children or sensitive readers. Many illustrations are available exclusively to Steady members. Are you a physician and interested in supporting this project? Join Steady to unlock full access to all images and enjoy an ad-free experience. Try it free for 7 days—no obligation.
New release: The first edition of the Urology Textbook as a Kindle e-book on Amazon—ideal for offline reading and quick reference. With over 1300 pages and hundreds of illustrations, it’s the perfect companion for residents and medical students.