You are here: Urology Textbook > Testes > Testicular trauma
Testicular Trauma: Injury of the Testes
Definition and Etiology of Testicular Trauma
Testicular trauma is an injury of the testes, usually caused by blunt force impact due to traffic accidents, fights, or sports injuries. Half of the direct, blunt injury leads to testicular rupture (tearing of the tunica albuginea). Swelling and intratesticular bleeding may cause progressive testicular ischemia with later atrophy if the tunica albuginea does not rupture. Less common are penetrating or degloving injury patterns.
Signs and Symptoms of Testicular Trauma
Testicular pain, scrotal hematoma, and soft tissue injuries depend on the etiology of testicular trauma.
Diagnostic Workup in Testicular Trauma
Ultrasonography of the Testes:
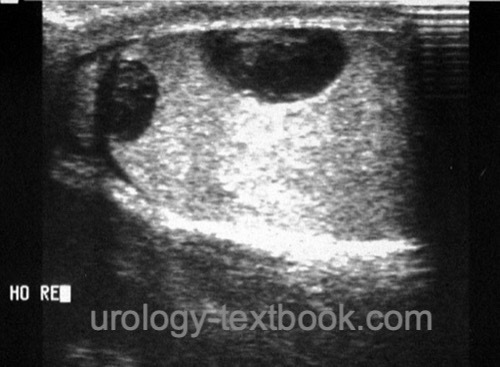
- Important is the localization of the hematoma, which can be scrotal, in the cavum serosum testis, or within the testicular parenchyma [fig. intratesticular hematoma].
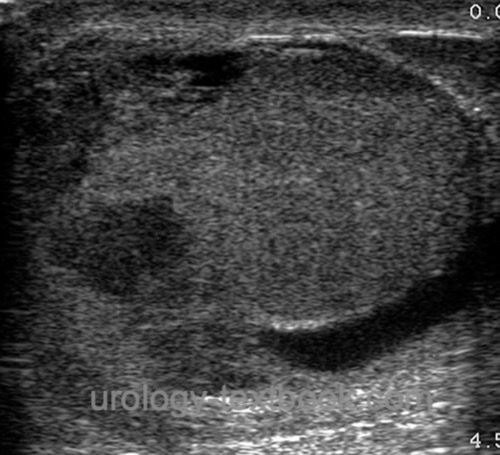
- The next important step in ultrasonography is the detection of a testicular rupture (tearing of the tunica albuginea) [fig. testicular rupture].
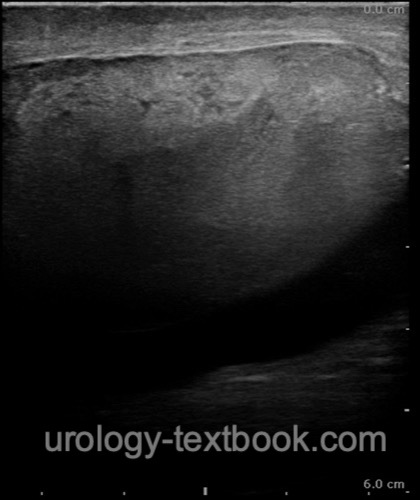
- Evaluate the testicular blood flow with Doppler sonography.
- The extent of injury is easily underestimated with testicular ultrasound imaging (Bhatt and Dogra, 2008). Inhomogeneities in the testicular parenchyma and evidence of a hematoma within the cavum serosum testis are signs of a rupture of the tunica albuginea, even if it appears intact.
 |
 |
 |
Treatment of Testicular Trauma
Conservative treatment of testicular injury:
Conservative treatment of testicular trauma is indicated for mild hematoma without tear of the tunica albuginea or decreased blood flow of the testis. Conservative treatment consists of analgesics, elevation of the scrotum, local cooling, and bed rest. Testicular ischemia or rupture due to swelling or bleeding may occur later in the course, regular follow-up is necessary.
Surgical Treatment of testicular injury:
Scrotal exploration is necessary for patients with significant hematoma (hematocele), with suspected testicular rupture, or if a decreased testicular blood flow is seen. Surgical treatment depends on the intraoperative findings: detorsion of the testis, removal of hematoma and nonviable tissue, and suture of the tunica albuginea. Orchiectomy is necessary for patients with complete testicular destruction.
| Do you want to see the illustration? Please support this website with a Steady membership. In return, you will get access to all images and eliminate the advertisements. Please note: some medical illustrations in urology can be disturbing, shocking, or disgusting for non-specialists. Click here for more information. |
| Do you want to see the illustration? Please support this website with a Steady membership. In return, you will get access to all images and eliminate the advertisements. Please note: some medical illustrations in urology can be disturbing, shocking, or disgusting for non-specialists. Click here for more information. |
| Do you want to see the illustration? Please support this website with a Steady membership. In return, you will get access to all images and eliminate the advertisements. Please note: some medical illustrations in urology can be disturbing, shocking, or disgusting for non-specialists. Click here for more information. |
| Do you want to see the illustration? Please support this website with a Steady membership. In return, you will get access to all images and eliminate the advertisements. Please note: some medical illustrations in urology can be disturbing, shocking, or disgusting for non-specialists. Click here for more information. |
| 46,XX male syndrome | Index | Epididymitis |
Index: 1–9 A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z
References
Bhatt, S. & Dogra, V. S.
Role of US in
testicular and scrotal trauma.
Radiographics, 2008,
28, 1617-1629
Buckley, J. C. & McAninch, J. W.
Diagnosis and
management of testicular ruptures.
Urol Clin North Am, 2006,
33, 111-6, vii
N. D. Kitrey, F. Campos-Juanatey, P. Hallscheidt, E. Serafetinidis, and D. M. Sharma, “EAU Guidelines: Urological Trauma,” 2022. [Online]. Available: https://uroweb.org/guidelines/urological-trauma/.
 Deutsche Version: Hodenverletzung
Deutsche Version: Hodenverletzung
Urology-Textbook.com – Choose the Ad-Free, Professional Resource
This website is designed for physicians and medical professionals. It presents diseases of the genital organs through detailed text and images. Some content may not be suitable for children or sensitive readers. Many illustrations are available exclusively to Steady members. Are you a physician and interested in supporting this project? Join Steady to unlock full access to all images and enjoy an ad-free experience. Try it free for 7 days—no obligation.
New release: The first edition of the Urology Textbook as an e-book—ideal for offline reading and quick reference. With over 1300 pages and hundreds of illustrations, it’s the perfect companion for residents and medical students. After your 7-day trial has ended, you will receive a download link for your exclusive e-book.