You are here: Urology Textbook > Urologic surgery > Subinguinal incision
Subinguinal Incision: Steps of the Surgical Approach
Urologic Indications
Inguinal lymphadenectomy in patients with:
Patient Positioning:
Supine position with slight abduction of the hip and flexion of the knee.
Surgical Technique of an Subinguinal Incision
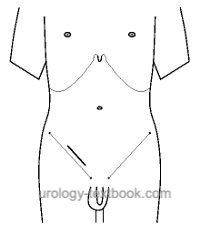
- Skin incision 3 cm below and parallel to the inguinal ligament, see fig. groin surgery
- Straight dissection of the subcutaneous tissue through the fascia of scarpa to the fascia lata. The skin should be dissected together with the subcutaneous tissue to preserve the supplying vessels.
- Identification and isolation of the great saphenous vein and superficial veins near the fossa ovalis (superficial epigastric, superficial iliac circumflex, and superficial external pudendal veins).
Wound Closure:
Redon drains, subcutaneous closure with interrupted sutures. Depending on the extend of dissection, myocutaneous flaps are necessary to cover the femoral vessels and to promote wound healing.
 |
| Inguinal incision | Index | Circumsising incision |
Index: 1–9 A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z
References
J. A. Smith, S. S. Howards, G. M. Preminger, and R. R. Dmochowski, Hinman’s Atlas of Urologic Surgery Revised Reprint. Elsevier, 2019.
 Deutsche Version: Operativer Zugang zu den inguinalen Lymphknoten
Deutsche Version: Operativer Zugang zu den inguinalen Lymphknoten
Urology-Textbook.com – Choose the Ad-Free, Professional Resource
This website is designed for physicians and medical professionals. It presents diseases of the genital organs through detailed text and images. Some content may not be suitable for children or sensitive readers. Many illustrations are available exclusively to Steady members. Are you a physician and interested in supporting this project? Join Steady to unlock full access to all images and enjoy an ad-free experience. Try it free for 7 days—no obligation.
New release: The first edition of the Urology Textbook as an e-book—ideal for offline reading and quick reference. With over 1300 pages and hundreds of illustrations, it’s the perfect companion for residents and medical students. After your 7-day trial has ended, you will receive a download link for your exclusive e-book.