You are here: Urology Textbook
Spermatocele: Causes, Symptoms and Treatment
Definition
Spermatoceles are cysts of the epididymis, which arise from the epididymal duct and contain sperm.
| Do you want to see the illustration? Please support this website with a Steady membership. In return, you will get access to all images and eliminate the advertisements. Please note: some medical illustrations in urology can be disturbing, shocking, or disgusting for non-specialists. Click here for more information. |
Epidemiology of Spermatoceles
The prevalence in ultrasound screening studies is 10%. The prevalence of spermatoceles increases with age (up to 30%).
Signs and Symptoms
- Painless testicular swelling
- Positive transillumination
- Seldom: disturbing size or pain
Diagnosis of Spermatoceles
Ultrasound imaging:
Testicular ultrasound imaging is used for the differential diagnosis of scrotal swelling. Spermatoceles present with an anechoic cystic mass in contact with the epididymis. Tubular ectasia of the rete testis (TERT) is associated with spermatocele.
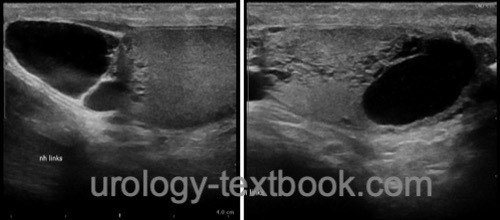 |
Treatment of Spermatoceles
Indication for surgery:
Disturbing size or pain.
Contraindications for surgery:
Patients with desire for children: Spermatocelectomy causes (with a high probability) sterility on the operated side. Delayed repair or cryopreservation of sperm is recommended if fertility is an issue.
Surgical technique of spermatocelectomy
The testis is delivered through a scrotal incision. Resect the spermatocele with careful dissection between the spermatocele and epididymis. The ligation of the final attachments of the spermatocele prevents granuloma formation. The operation is finished with the closure of the tunica vaginalis, tunica dartos (subcutaneous suture), and scrotal skin. Please see section spermatocelectomy for details. Epididymectomy is performed if multiple cysts are present.
Puncture of the Spermatocele with Sclerotherapy
Sclerotherapy of spermatoceles is not a standard therapy and has been tested only in small studies.
| Hydrocele | Index | Male hypogonadism |
Index: 1–9 A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z
References
Rubenstein u.a. 2004 RUBENSTEIN, R. A. ;
DOGRA, V. S. ; SEFTEL, A. D. ; RESNICK, M. I.:
Benign intrascrotal lesions.
In: J Urol
171 (2004), Nr. 5, S. 1765–72
 Deutsche Version: Spermatozele: Ursachen und Therapie
Deutsche Version: Spermatozele: Ursachen und Therapie
Urology-Textbook.com – Choose the Ad-Free, Professional Resource
This website is designed for physicians and medical professionals. It presents diseases of the genital organs through detailed text and images. Some content may not be suitable for children or sensitive readers. Many illustrations are available exclusively to Steady members. Are you a physician and interested in supporting this project? Join Steady to unlock full access to all images and enjoy an ad-free experience. Try it free for 7 days—no obligation.
New release: The first edition of the Urology Textbook as an e-book—ideal for offline reading and quick reference. With over 1300 pages and hundreds of illustrations, it’s the perfect companion for residents and medical students. After your 7-day trial has ended, you will receive a download link for your exclusive e-book.