You are here: Urology Textbook > Prostate > Prostatitis > Acute bacterial prostatitis
Diagnosis and Treatment of Bacterial Prostatitis
Definitions
Acute prostatitis is a bacterial infection of the prostate with sudden fever, perineal and suprapubic pain, and voiding symptoms. Chronic bacterial prostatitis refers to persistent or recurrent bacterial prostatitis for more than three months (Benway and Moon, 2008). EAU Guidelines: Urological Infections.
Etiology of Bacterial Prostatitis
Intraprostatic reflux:
Urine and bacteria may enter via reflux into the prostate and lead to inflammation. In the biofilm of the prostate stones, bacteria can persist despite adequate antibiotic treatment or inflammatory response and maintain a chronic infection.
Pathogens:
Acute prostatitis is a bacterial infection of the prostate caused by the ascension of bacteria from the urinary tract. Predominant pathogens are E. coli and other enterobacteriaceae, Enterococcus and Staphylococcus. Consider Neisseria gonorrhoeae and Chlamydia trachomatis in sexually active men. Uncommon causes are Mycobacterium tuberculosis or BCG. Risk factors for acute prostatitis are intraprostatic reflux, phimosis, anal sex, urinary tract infections, epididymitis, bladder catheterization, prostate biopsy, and transurethral resections.
Chronic bacterial infection: among other Enterobacteria, Chlamydia trachomatis, Ureaplasma urealyticum. The detection of pathogens responsible for prostatitis is difficult since contamination from the urethra, and non-pathogenic bacteria in the prostate, are common.
Pathology of Acute Prostatitis
Macroscopic Pathology
- Enlarged prostate
- Hyperemia and edema
- Abscess formation
Microscopic Pathology
- Infiltration by neutrophils in acinar and stromal tissue
- Microabscesses
Signs and Symptoms
General complaints:
Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms:
- Urinary frequency and urgency
- Dysuria
- Weak urinary stream and urinary retention
Rectal Examination
Painful prostate exam: prostate of soft consistency, possibly with fluctuation as a sign of a prostate abscess.
Diagnostic Workup of Bacterial Prostatitis
Microbiological diagnosis of acute prostatitis:
The urine sediment shows pyuria, bacteriuria and microhematuria. Urine culture usually identifies the pathogen and is thus obligatory before starting antibiotic therapy. A blood culture can identify the pathogen if a high fever or signs of urosepsis are present.
Microbiological diagnosis of chronic prostatitis:
In order to identify chronic bacterial prostatitis, four separate specimens (4-glass test) are collected and examined microbiologically with urine sediment microscopy and culture. Bacterial prostatitis is diagnosed if there is a 10-fold increase in bacteria between VB1/2 and EPS/VB3:
- The first 10 ml of urine (urethral specimen, VB1)
- Midstream urine (bladder specimen, VB2)
- Expressed prostate secret (EPS)
- The first 10 ml of urine after prostatic massage (prostate specimen VB3)
Due to the high costs and effort, a two-glass test has become standard; recent studies have confirmed the equivalence:
- Midstream urine (bladder specimen)
- The first 10 ml of urine after prostatic massage (prostate specimen)
Blood Tests
Ultrasound Imaging
Ultrasound imaging of the bladder: Urinary retention or residual urine?
Transrectal ultrasound imaging
After initiating the antibiotic treatment, transrectal imaging can be safely performed and may reveal an abscess of the prostate [fig. prostatic abscess]. Alternative imaging is possible with a CT scan.
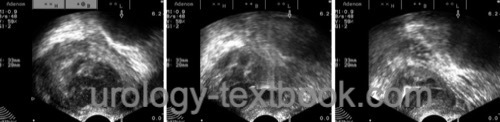 |
Treatment of Acute Prostatitis
Antibiotic therapy
Until the results of urine culture and blood culture are available, treatment is started with e.g., ofloxacin 200–400 mg p.o. 1-0-1 or ciprofloxacin 500 mg p.o. 1-0-1. Fluoroquinolones have a high antibacterial activity in oral doses and show a good tissue penetration.
In case of severe prostatitis, choose intravenous therapy: ampicillin/clavulanic acid 2.2 g 1-1-1 i.v., cephalosporin i.v. combined with gentamicin 3 mg/kg i.v. 1-0-0, or broad spectrum antibiotics like imipenem or meropenem.
Duration of Antibiotic Therapy
Antibiotic treatment is given parenterally for 3–7 days. Afterward, treatment is switched to a full-dose oral antibiotic for 2–4 weeks.
Symptomatic Treatment
- Suprapubic catheter drainage is necessary for urinary retention or refractory fever.
- Bed rest
- Rehydration
- Treatment of fever and pain with NSAID, e.g., diclofenac or metamizole
- Lactulose for stool softening
Prostatic Abscess
- Needle aspiration is sufficient in a small prostatic abscess
- Perineal drainage (Pigtail 8–12 CH) for large prostate abscess formation [fig. prostatic abscess]
- Transurethral resection and deroofing of central prostate abscess formation
Chronic bacterial prostatitis:
Oral long-term antibiotic therapy for 4–6 weeks, depending on the bacterial culture of urine or expressed prostate secretions.
Gramnegative bacteria:
Fluoroquinolones like ofloxacin 200–400 mg 1-0-1 or ciprofloxacin 250–500 mg 1-0-1.
Chlamydia trachomatis:
Azithromycin (1 g once a week), doxycyclin 100 mg 1-0-1.
Ureaplasma urealyticum:
Erythromycin 500 mg 1-1-1-1, fluoroquinolones.
Lack of improvement or recurrence:
Consider low-dose long-term antibiotics for prophylaxis in case of proven recurrence. TURP is an option in refractory cases, but controlled studies are lacking. Acute or chronic bacterial prostatitis may trigger chronic pelvic pain syndrome (CPPS); see next section.
| Prostatitis Definitionen | Index | Prostate diseases |
Index: 1–9 A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z
References
Benway, B. M. & Moon, T. D.
Bacterial prostatitis.
Urol Clin North Am, 2008, 35, 23-32;
G. Bonkat, R. Bartoletti, F. Bruyère, S. E. Geerlings, F. Wagenlehner, and B. Wullt, “EAU Guideline: Urological Infections.” [Online]. Available: https://uroweb.org/guidelines/urological-infections/
Krieger u.a. 1999 KRIEGER, J. N. ; NYBERG,
Jr. ; NICKEL, J. C.:
NIH consensus definition and classification of prostatitis.
In: Jama
282 (1999), Nr. 3, S. 236–7
Nickel 2003 NICKEL, J. C.:
Recommendations for the evaluation of patients with prostatitis.
In: World J Urol
21 (2003), Nr. 2, S. 75–81
 Deutsche Version: Akute bakterielle Prostatitis
Deutsche Version: Akute bakterielle Prostatitis